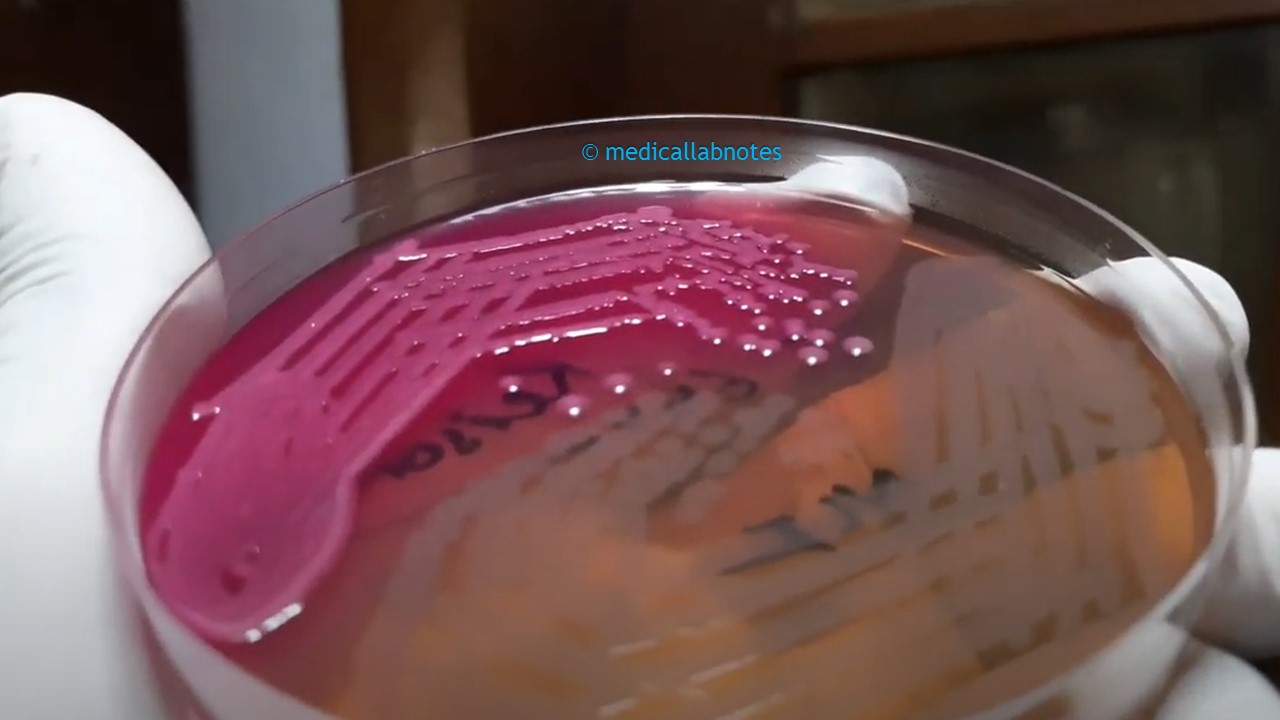
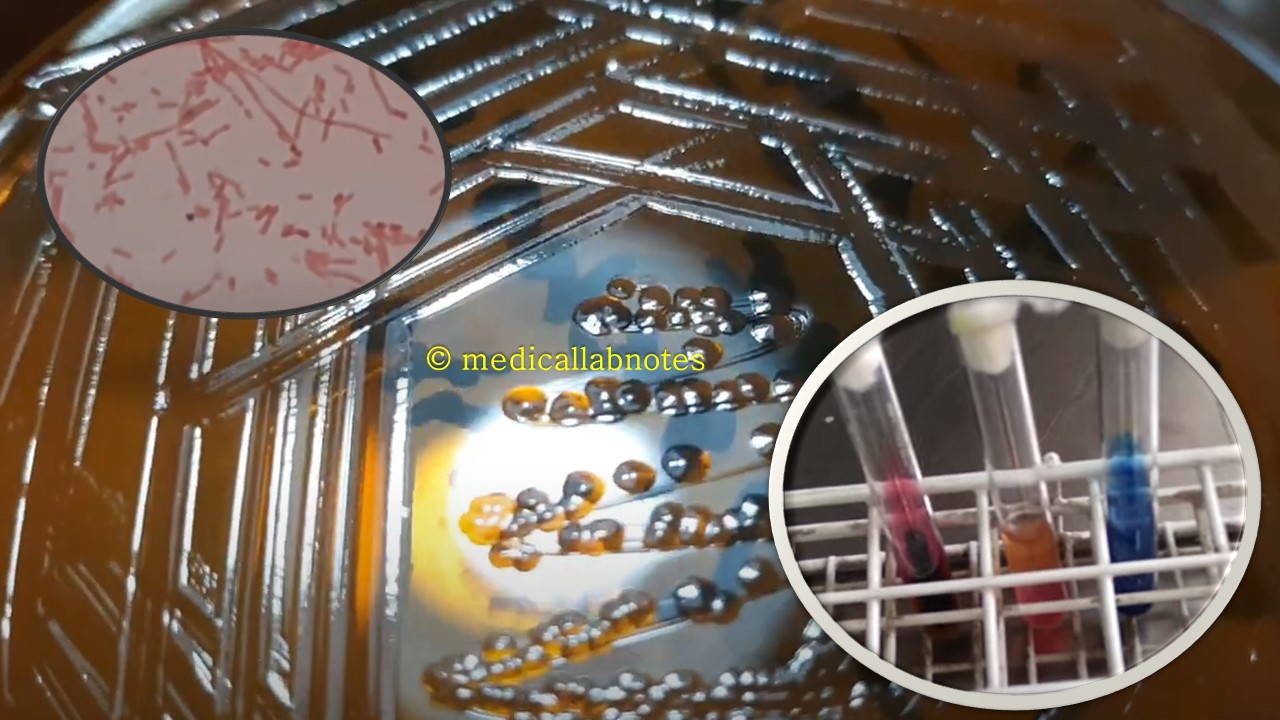
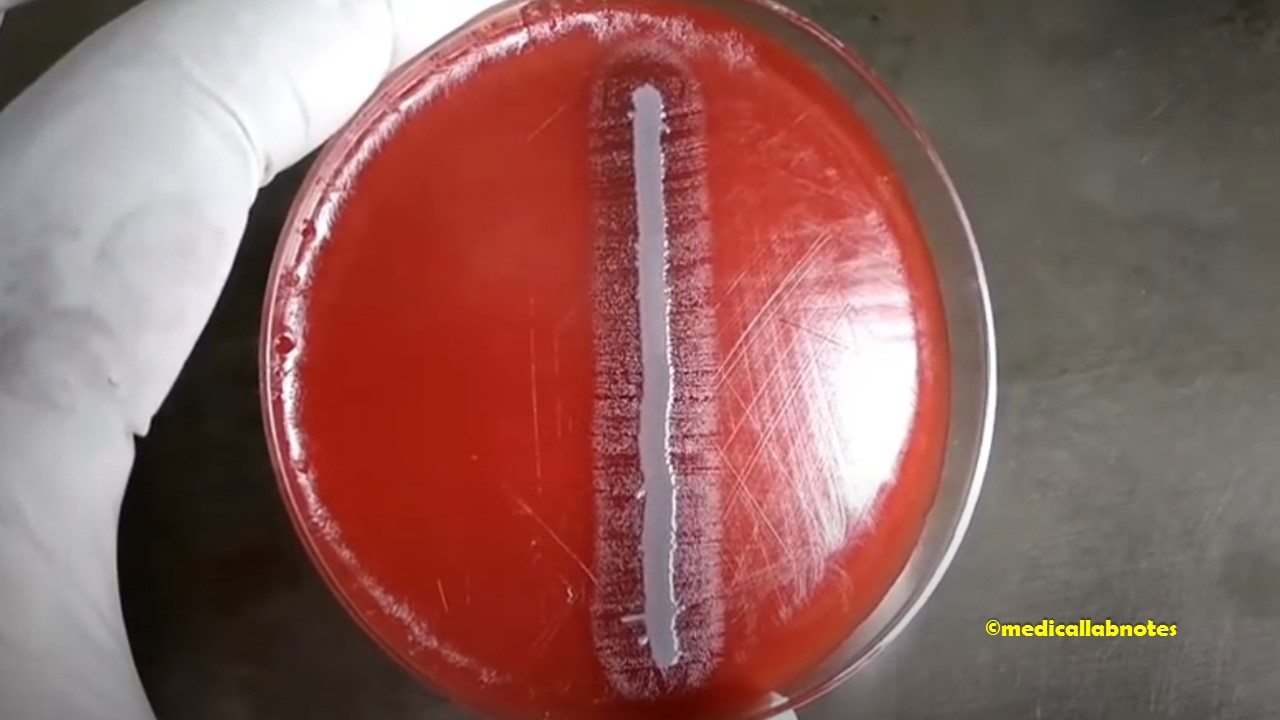
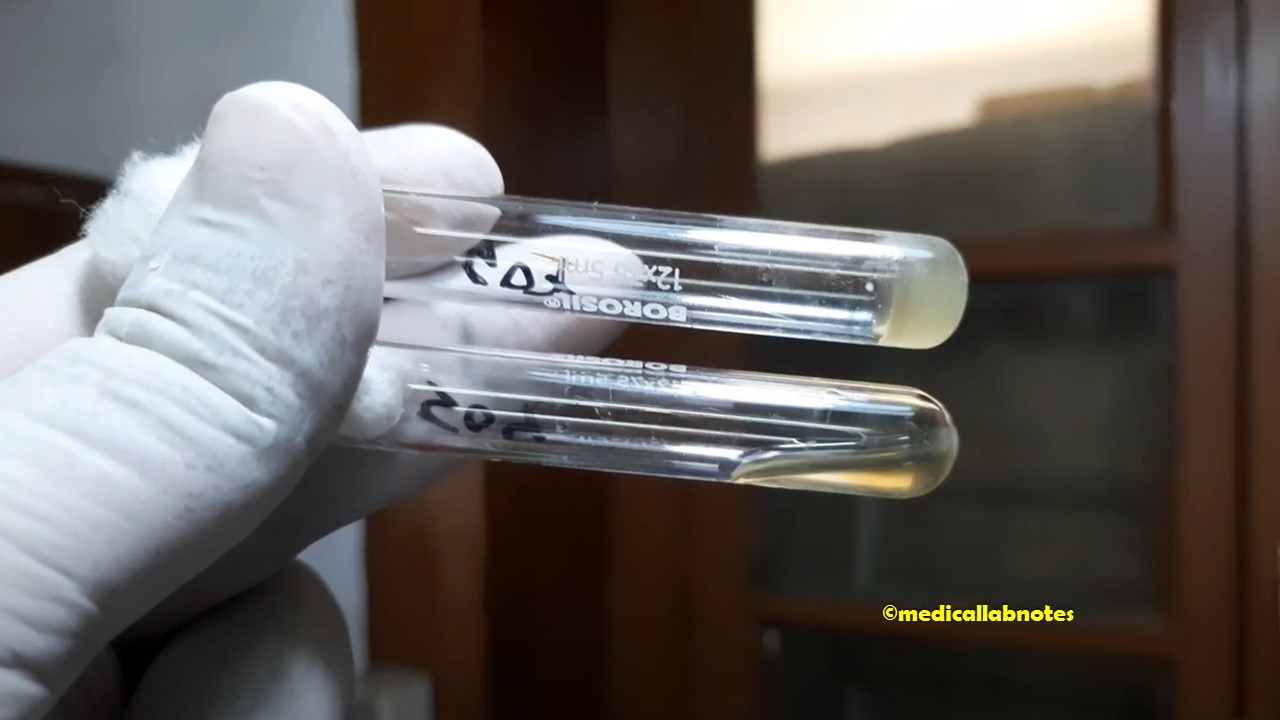
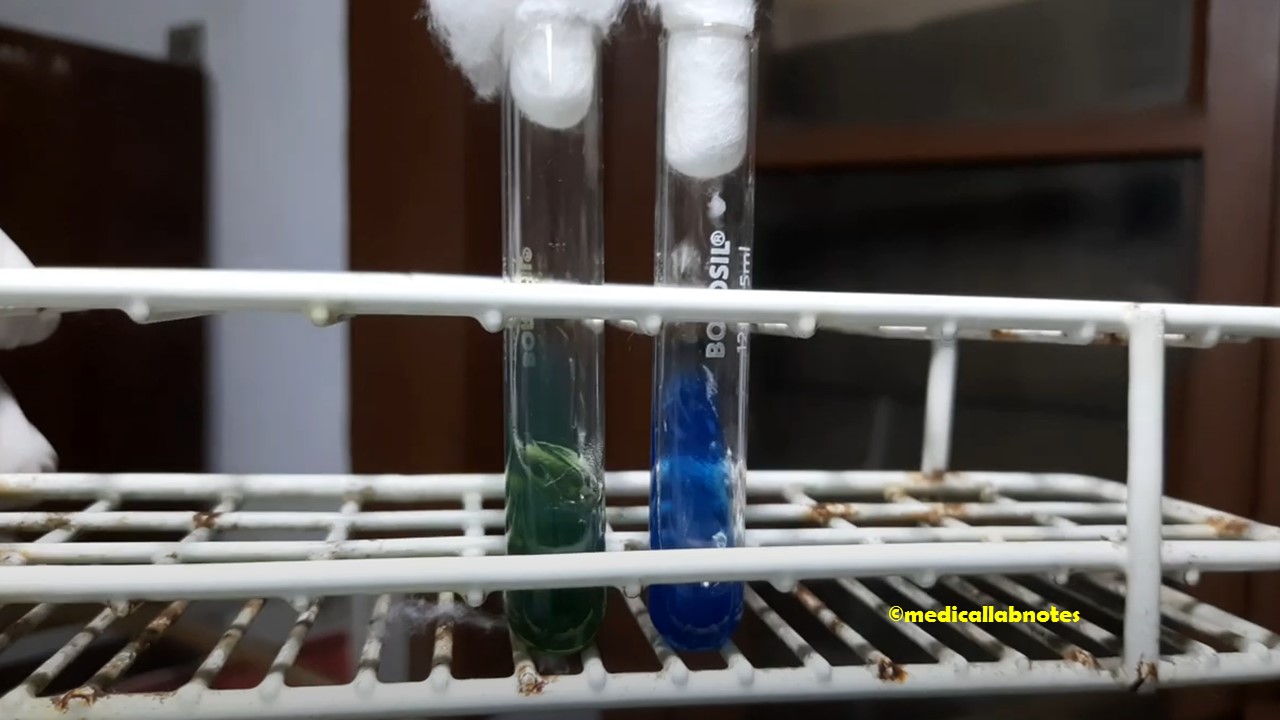
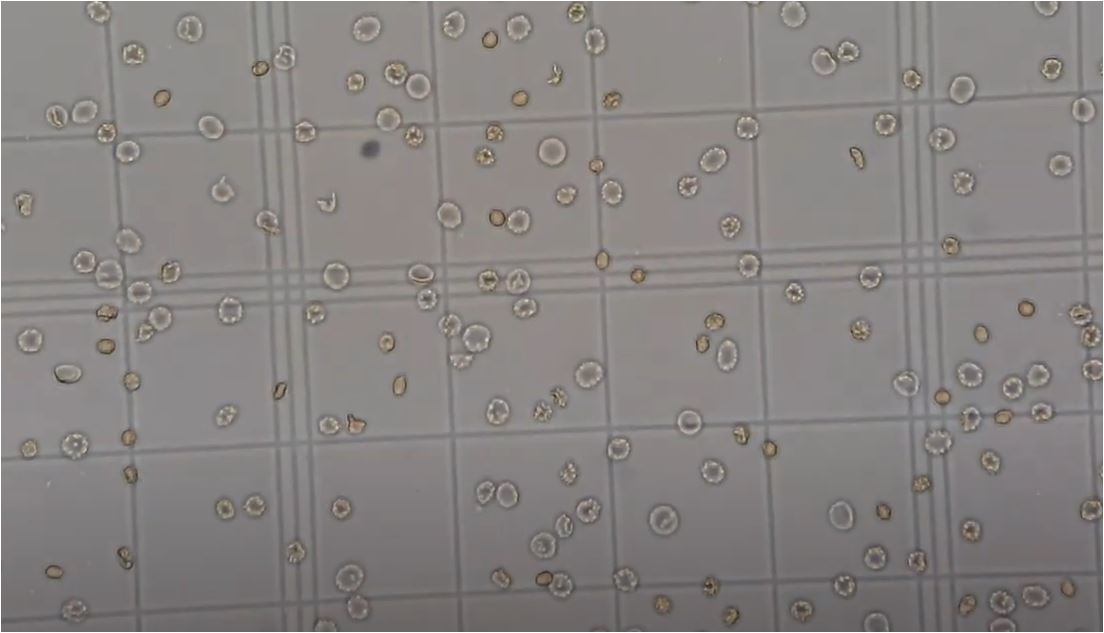
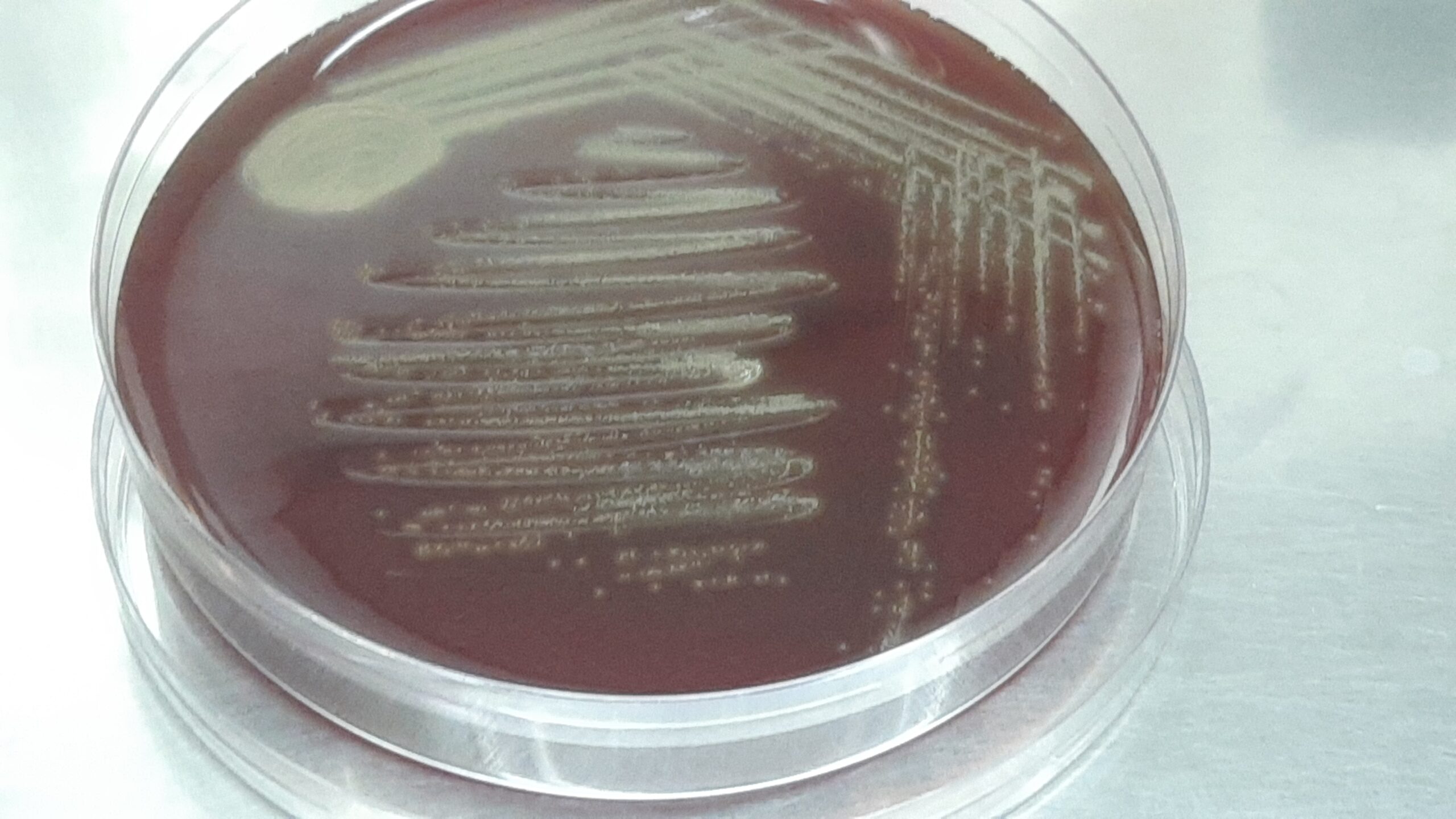
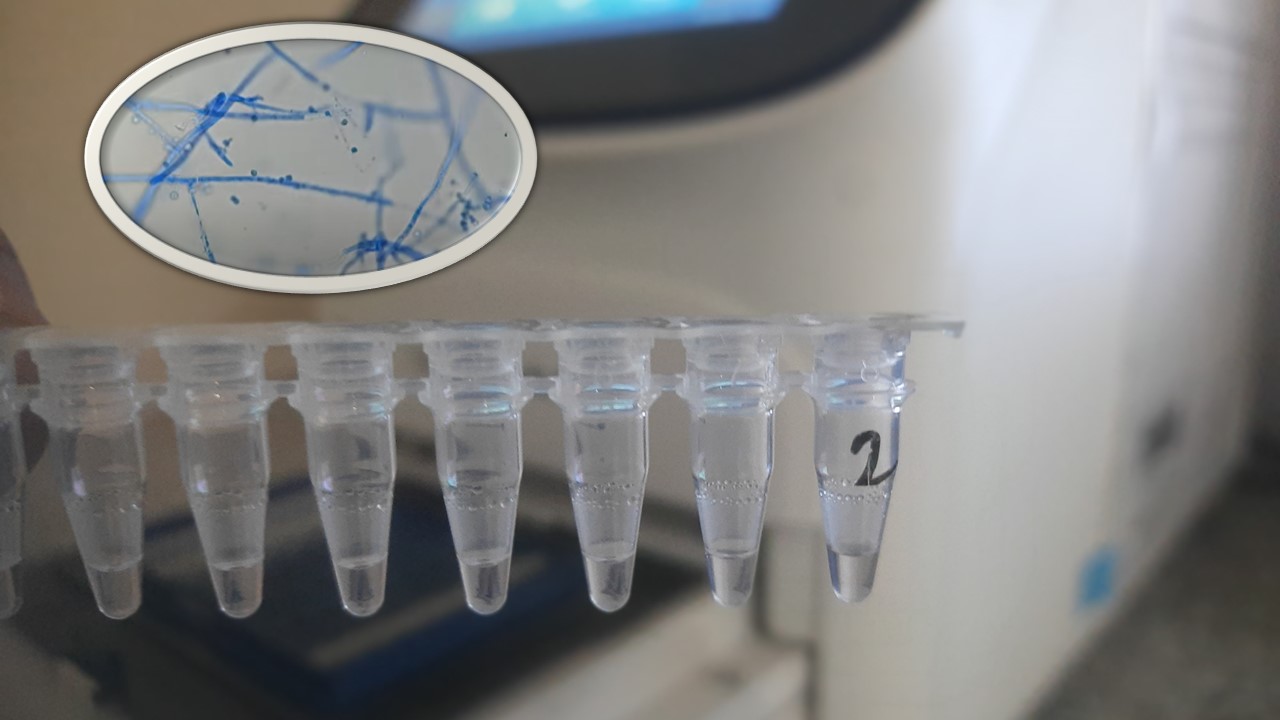
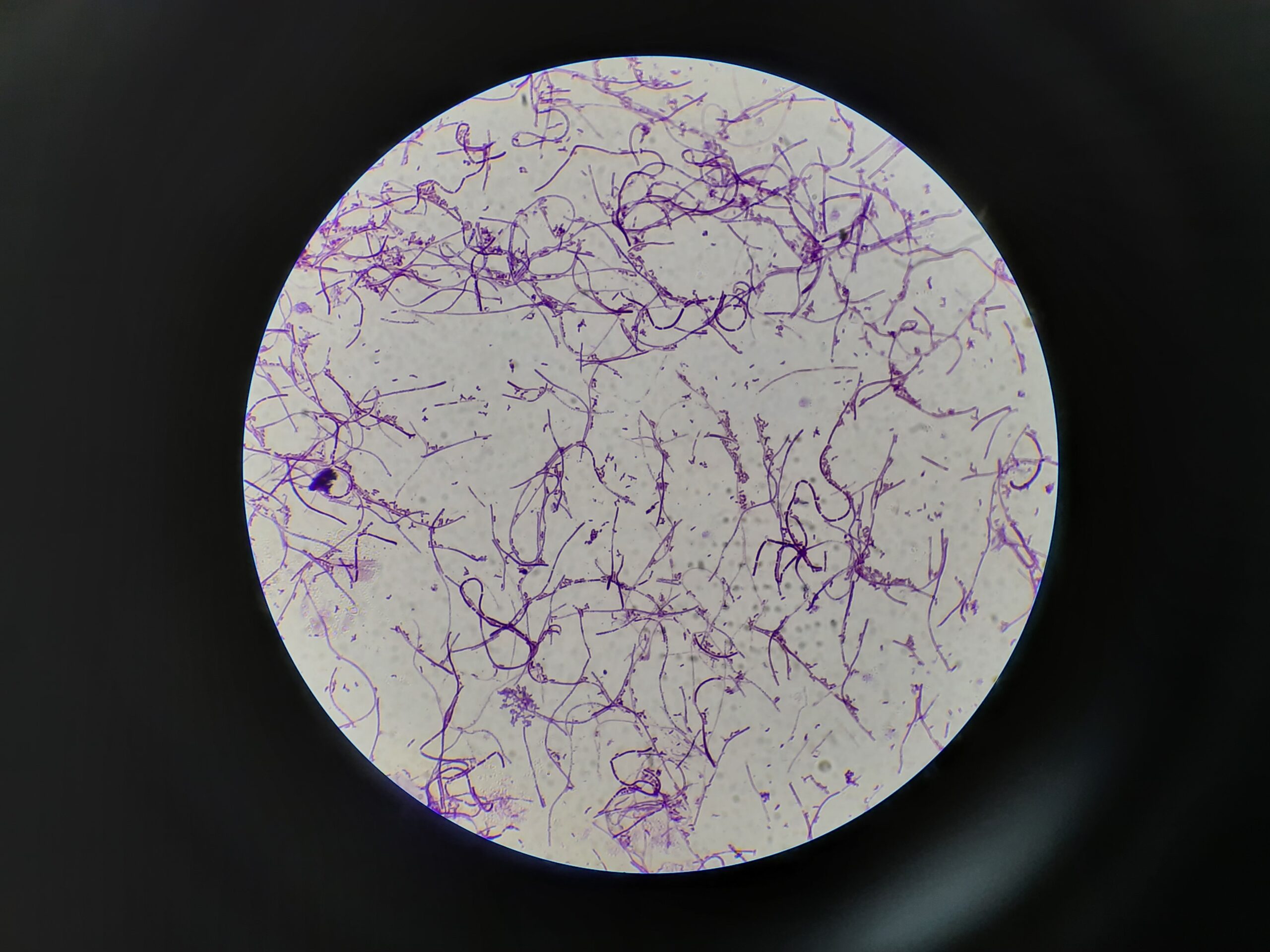
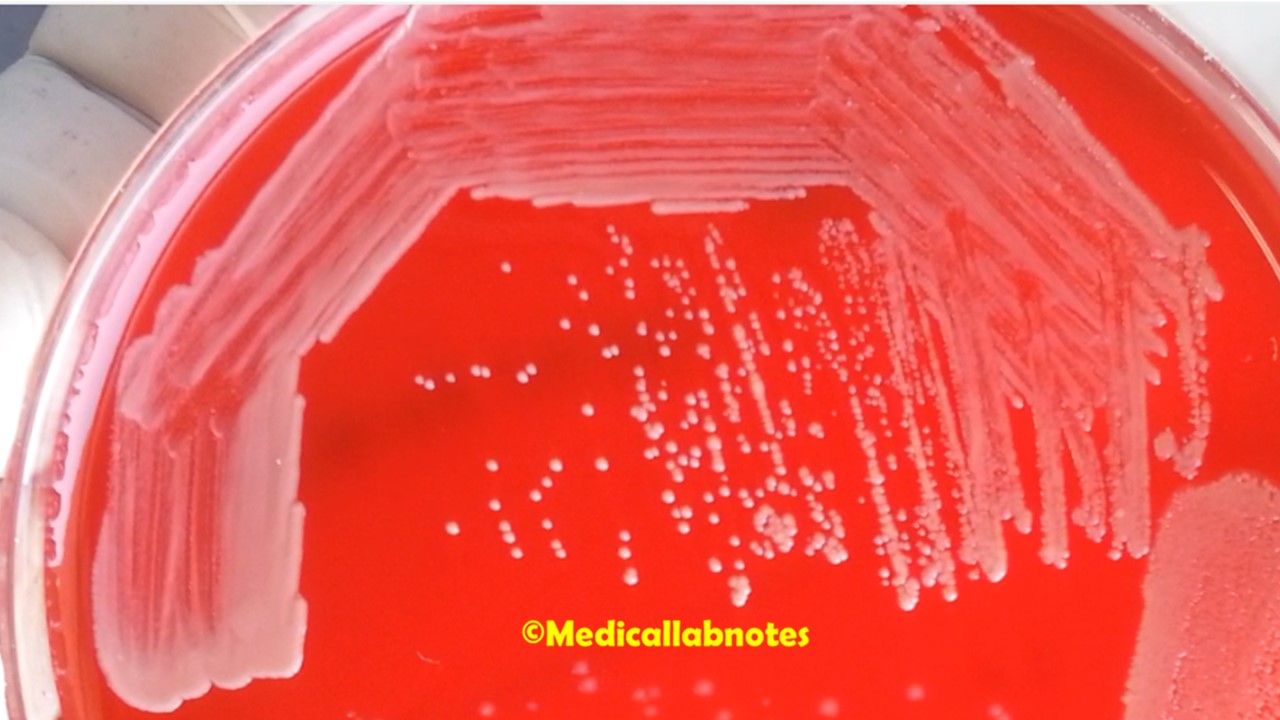
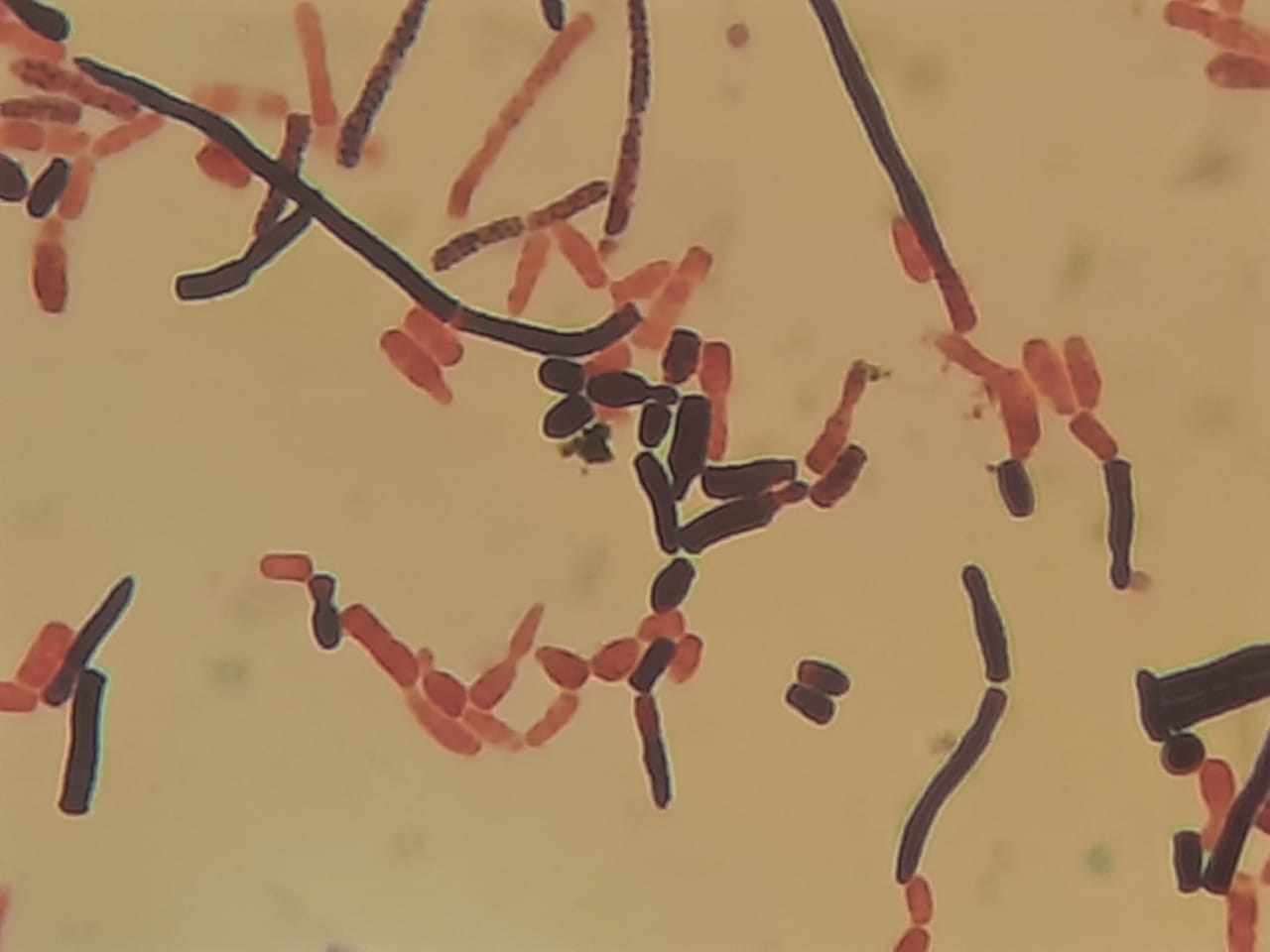
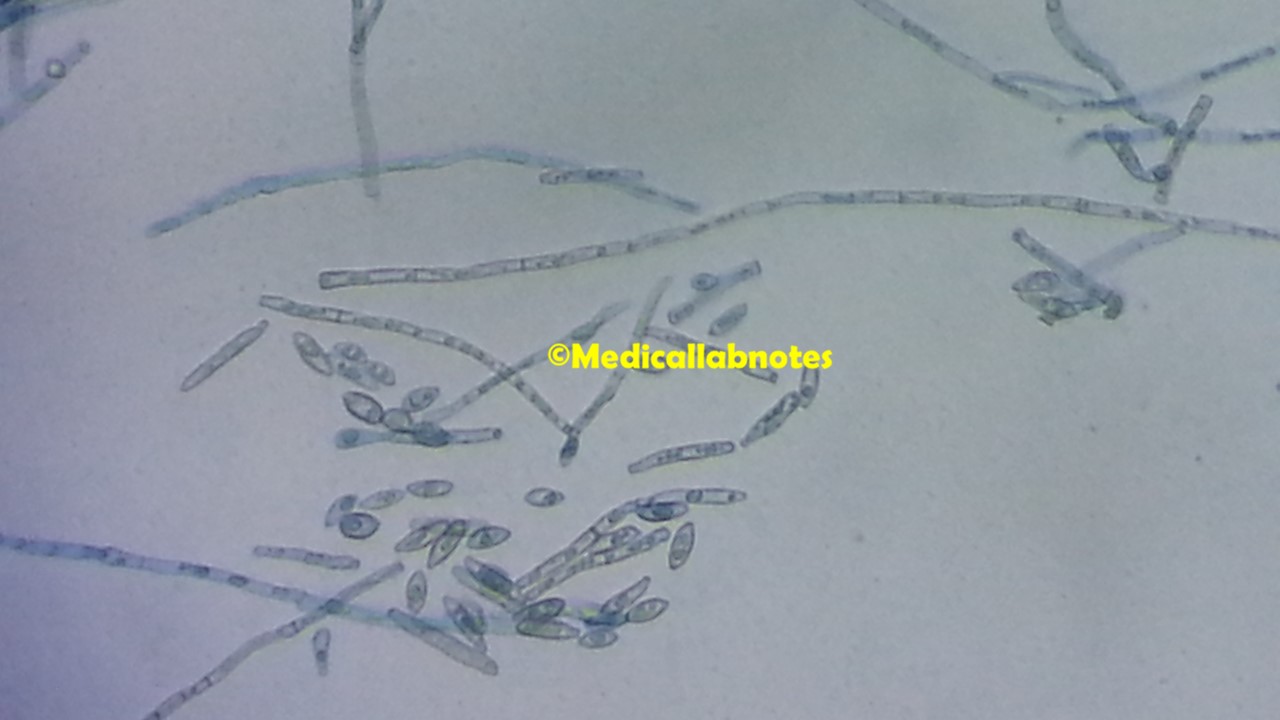
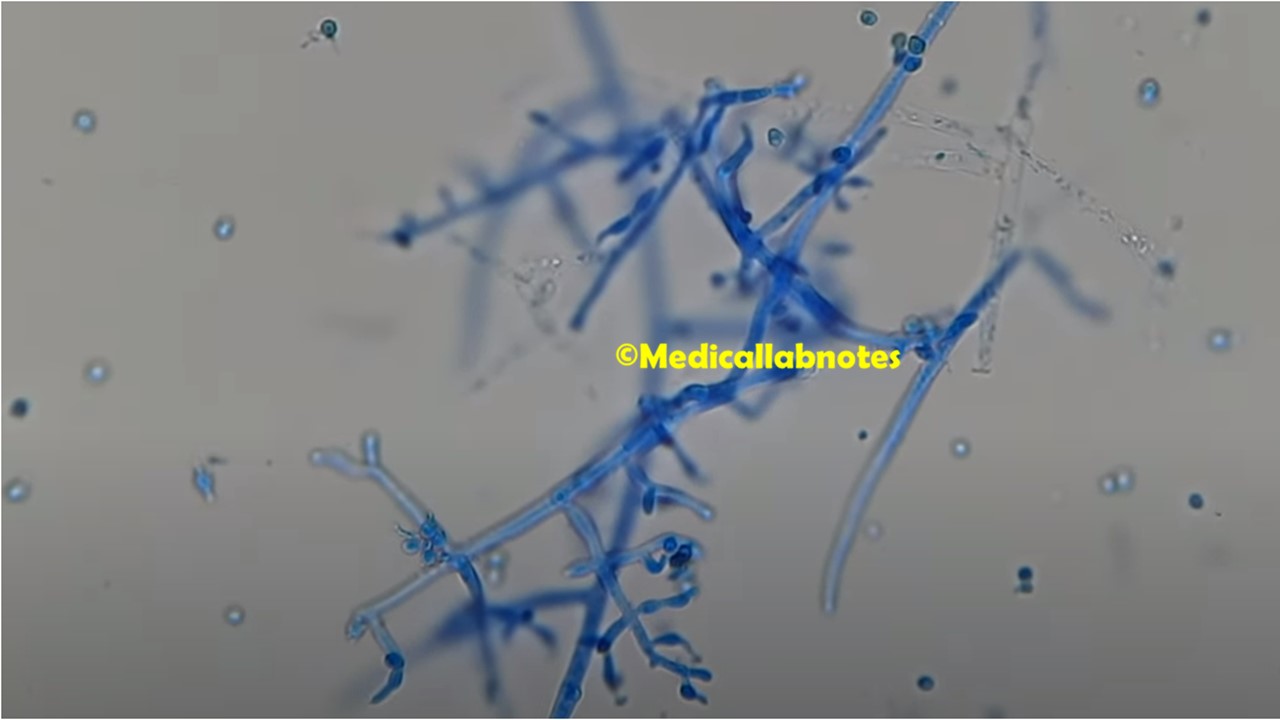
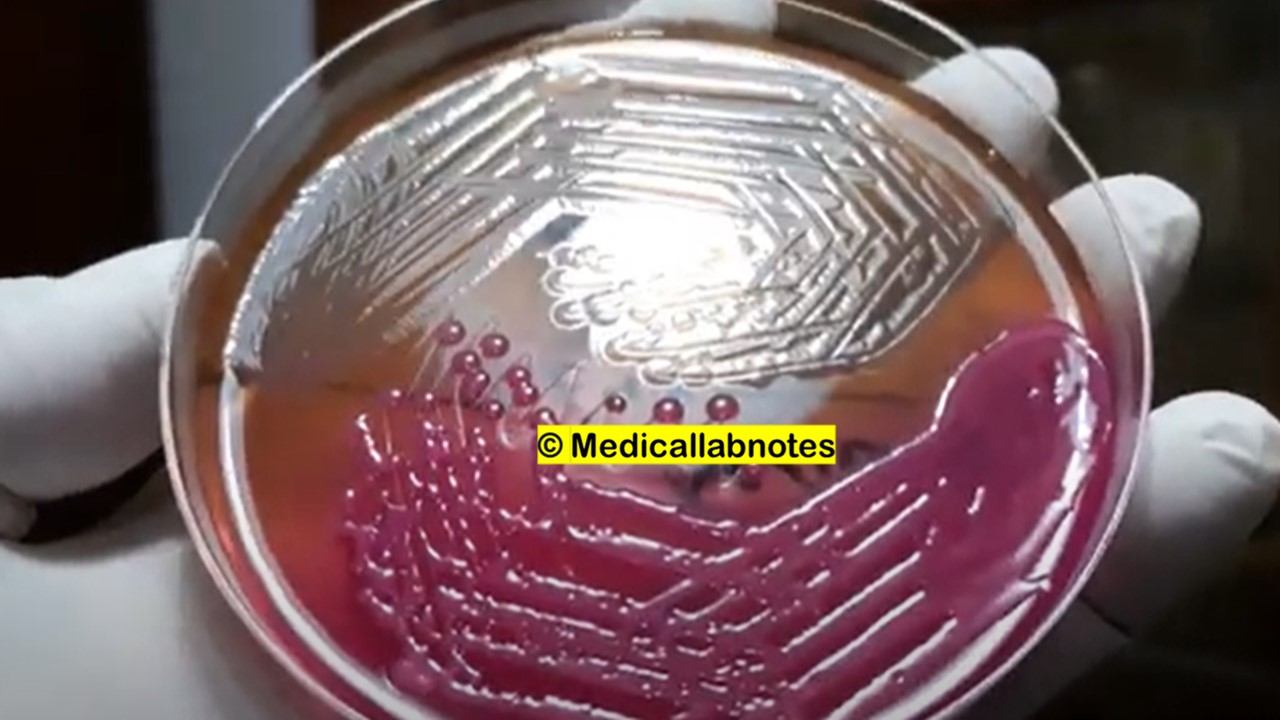
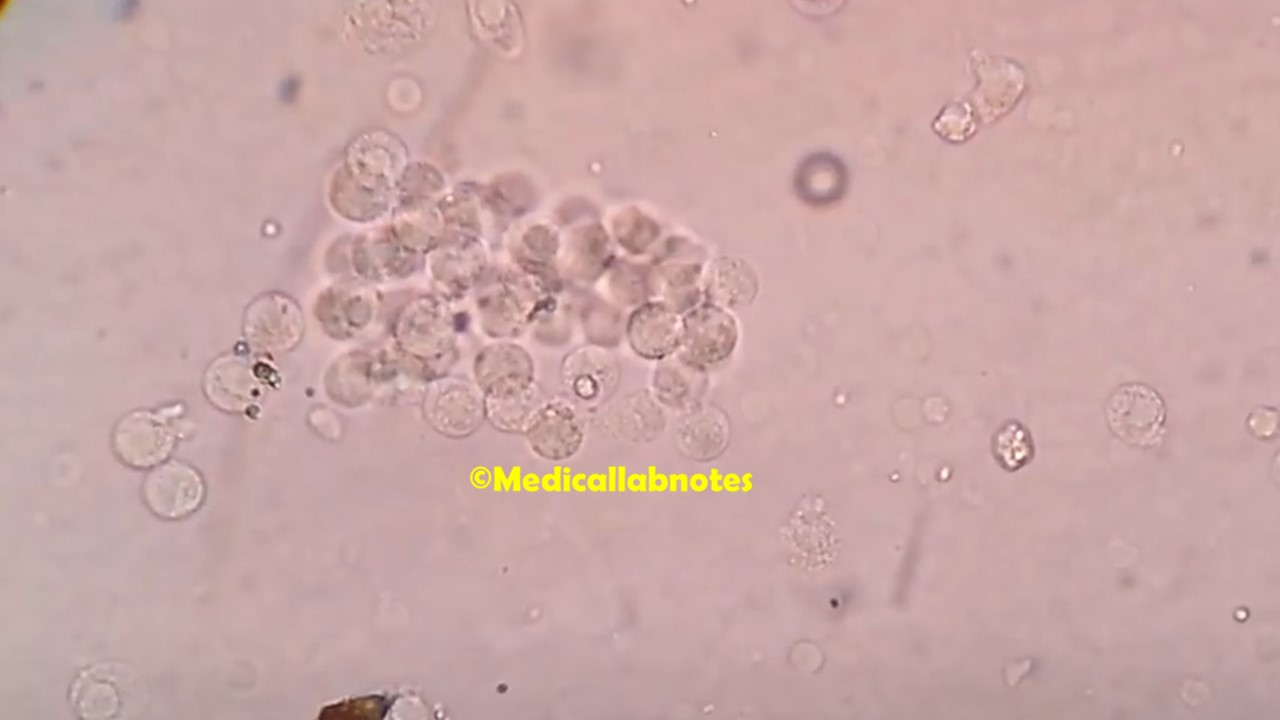
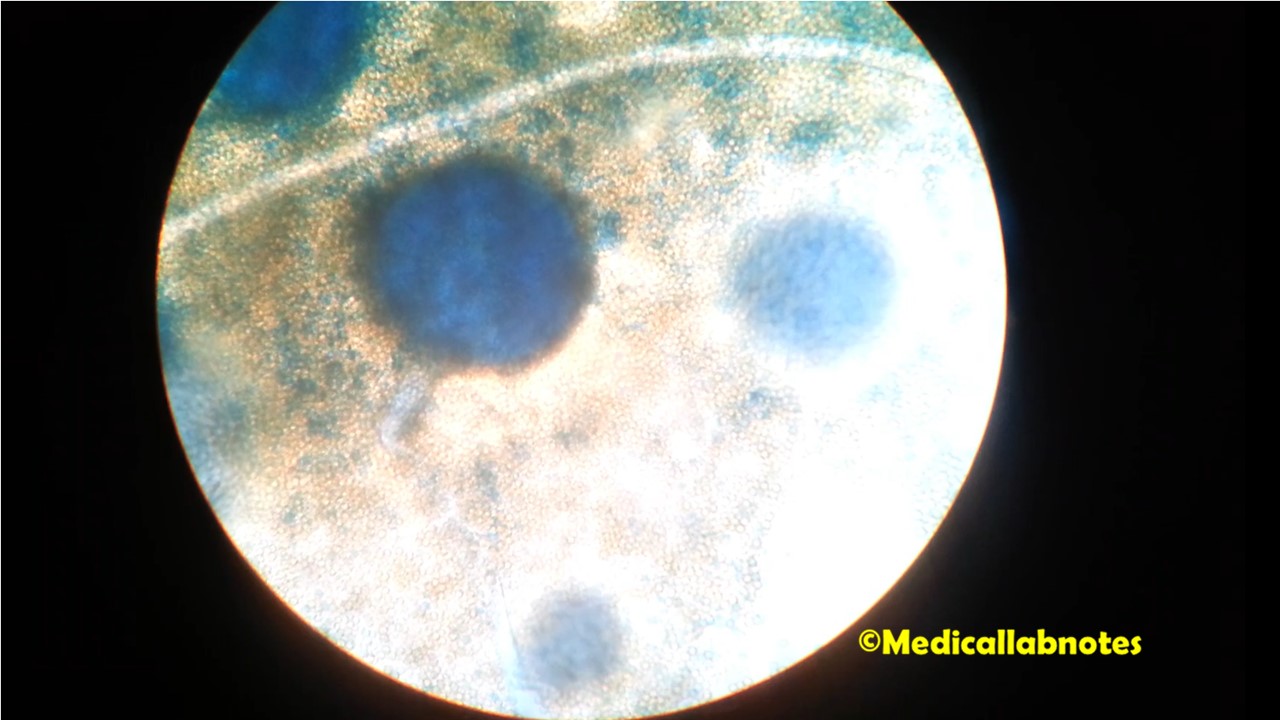
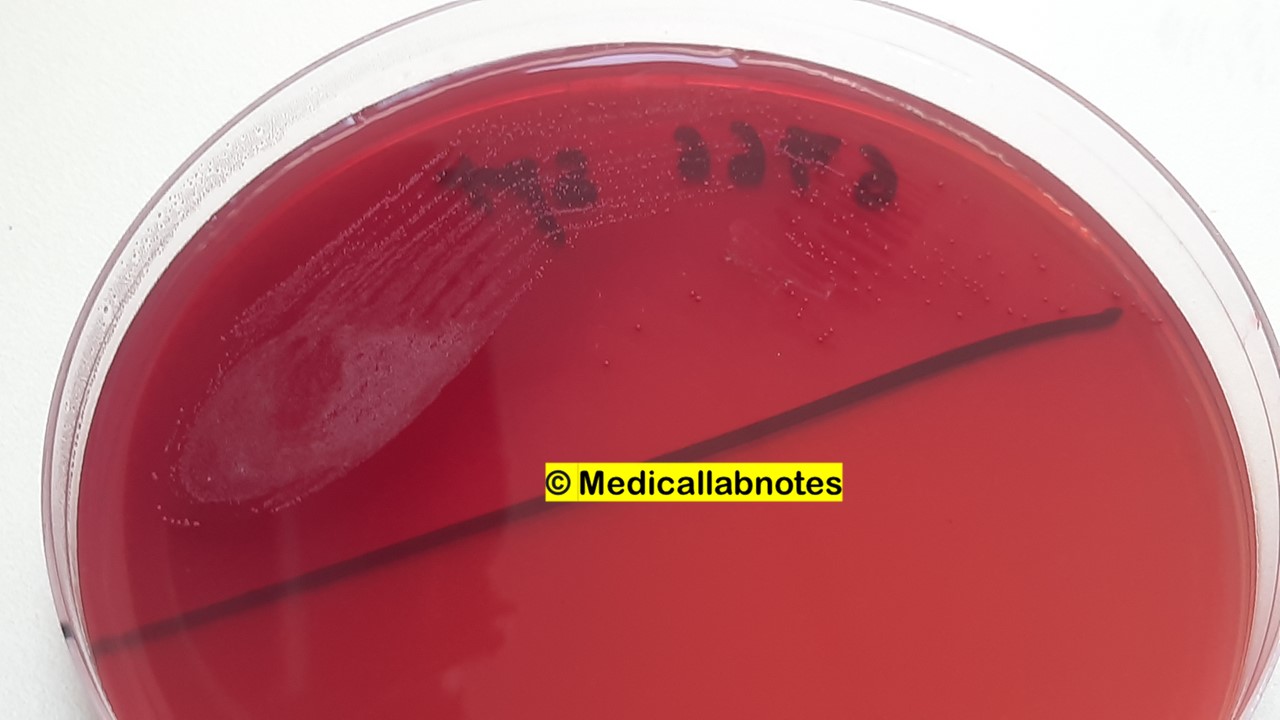
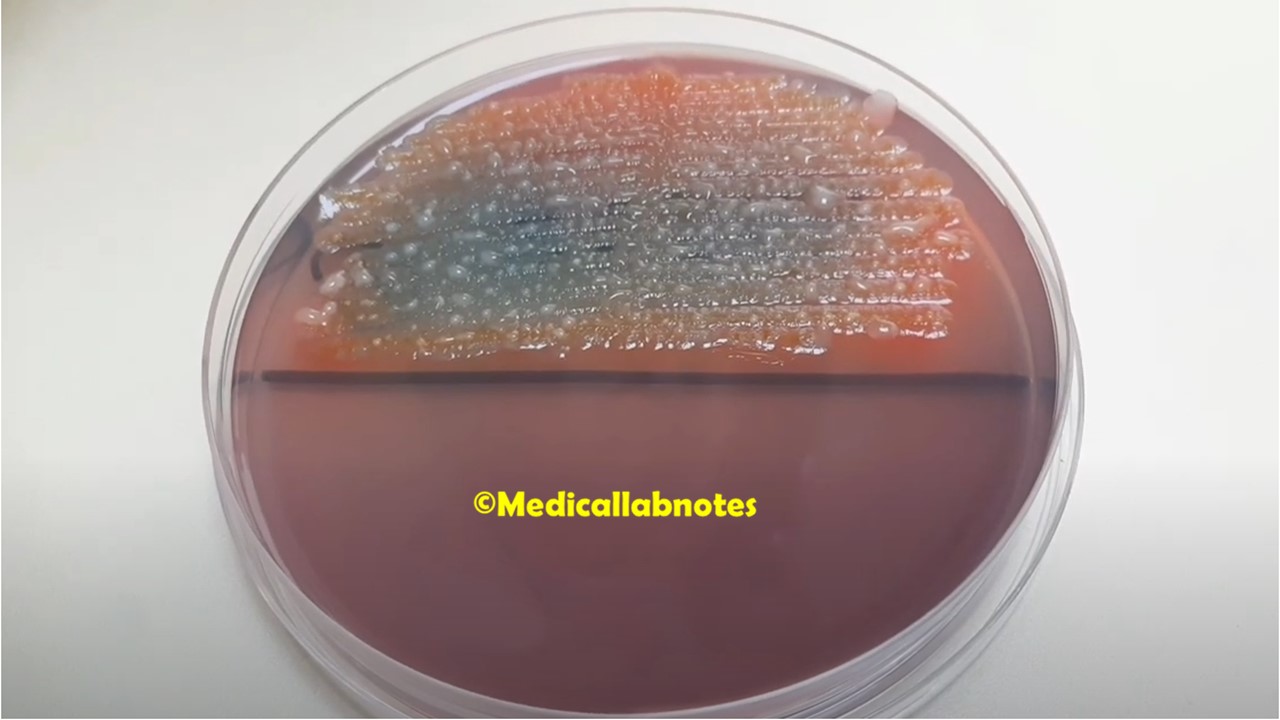
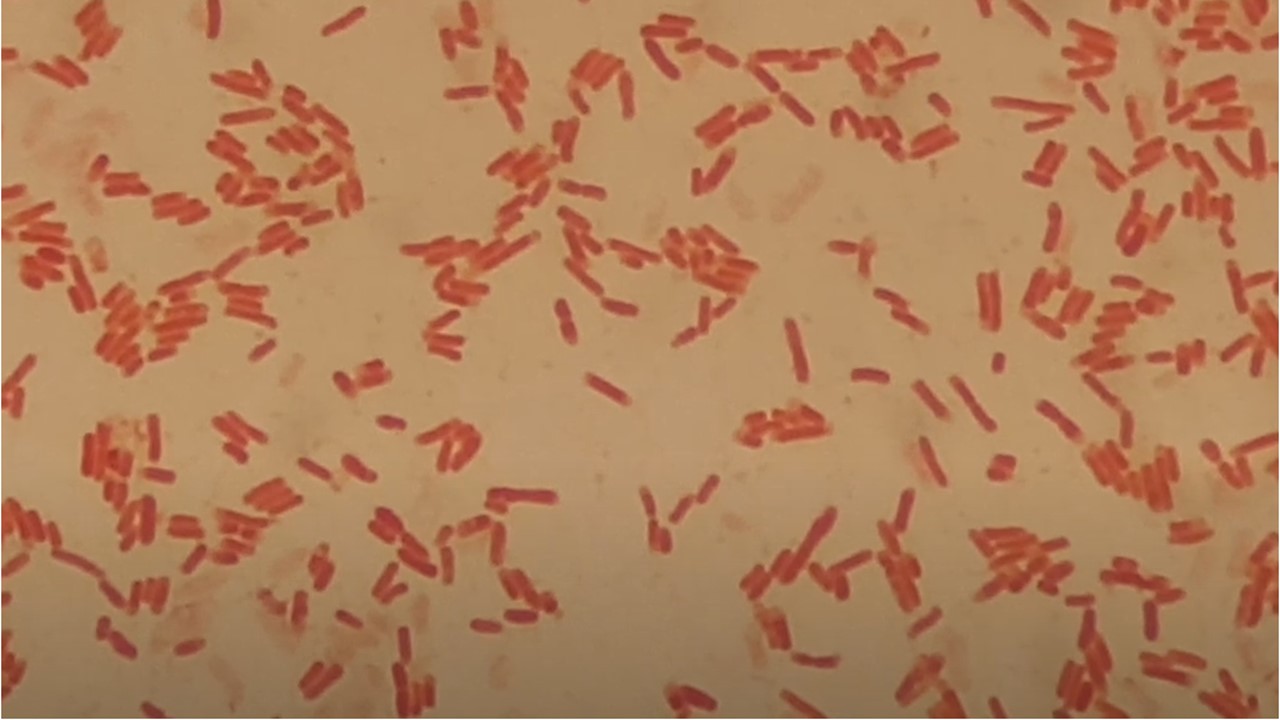
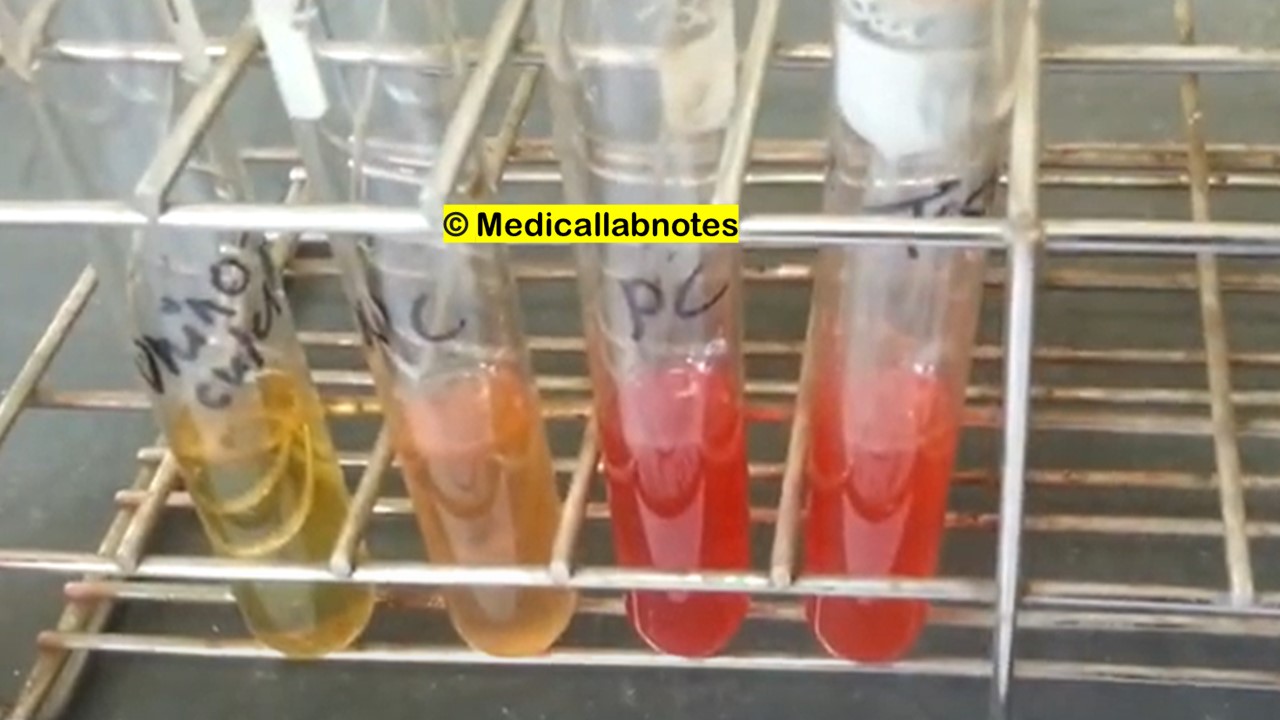
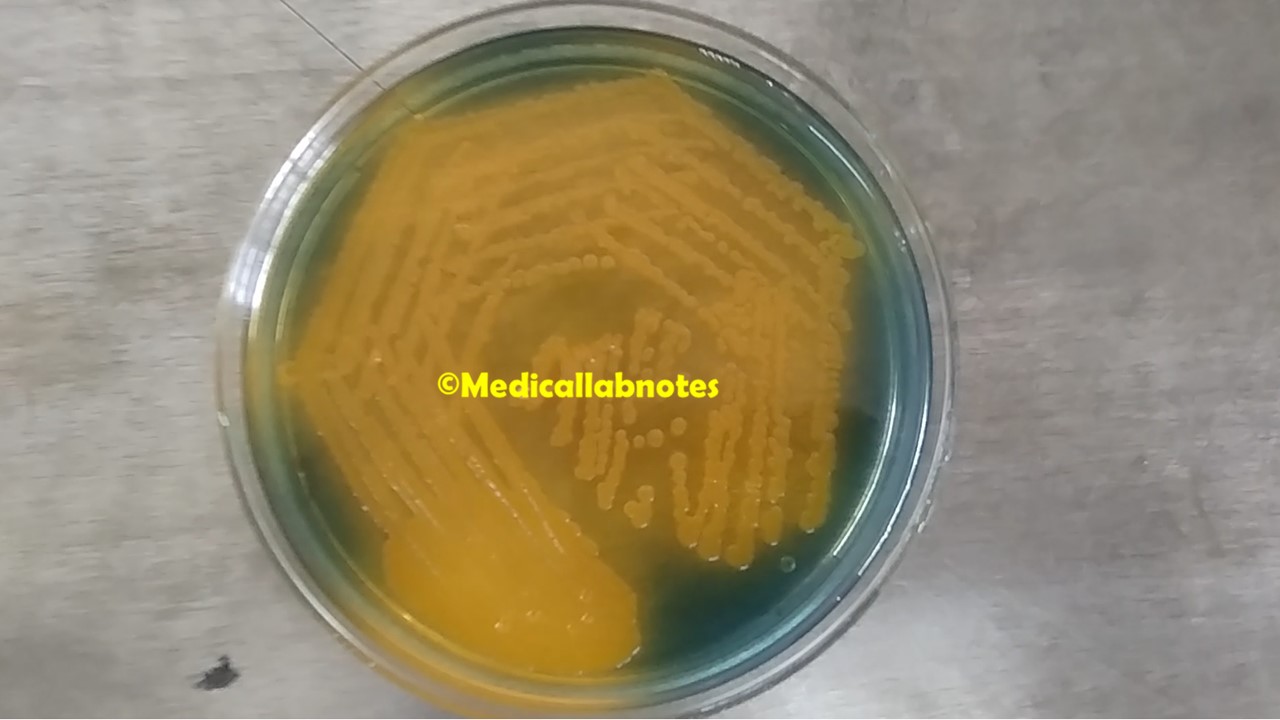
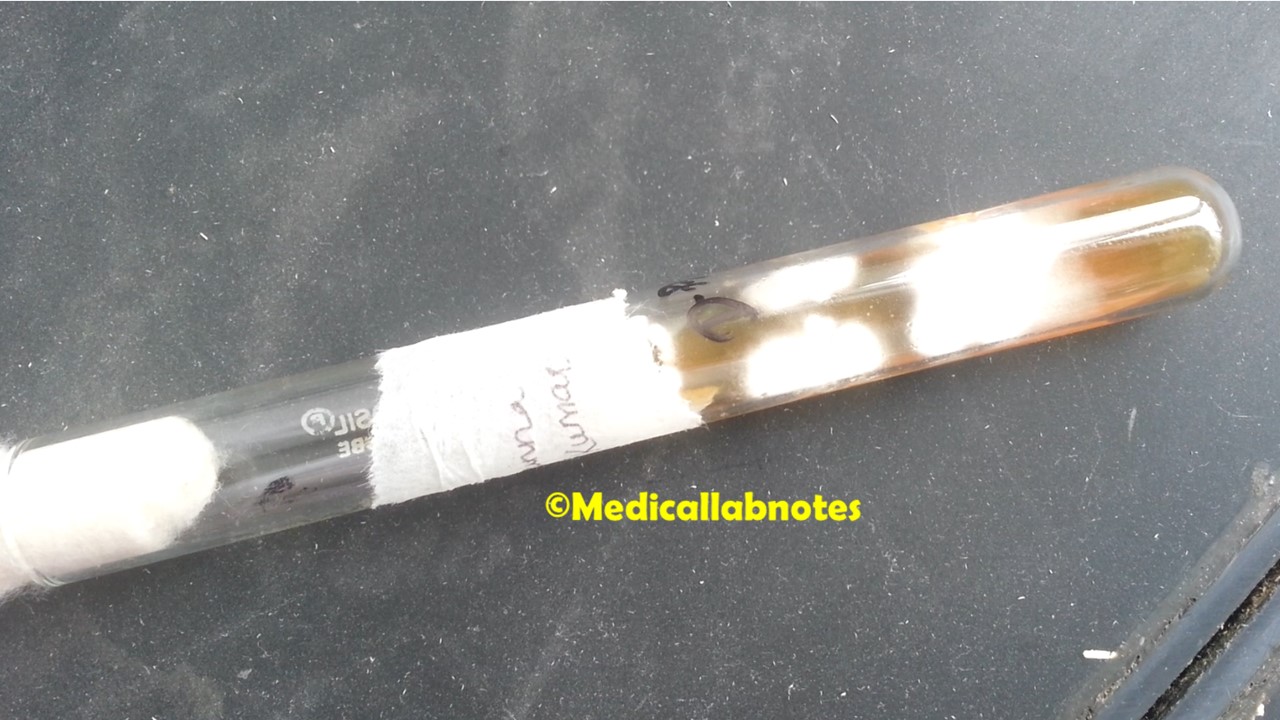
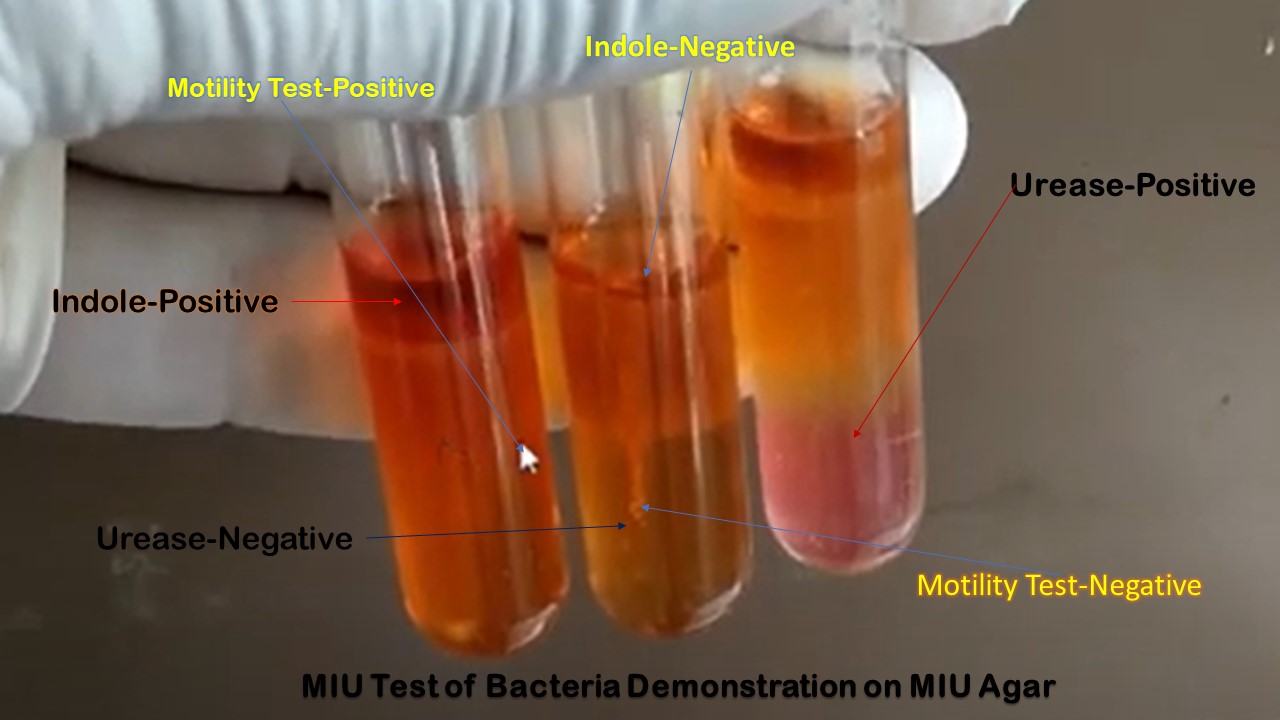
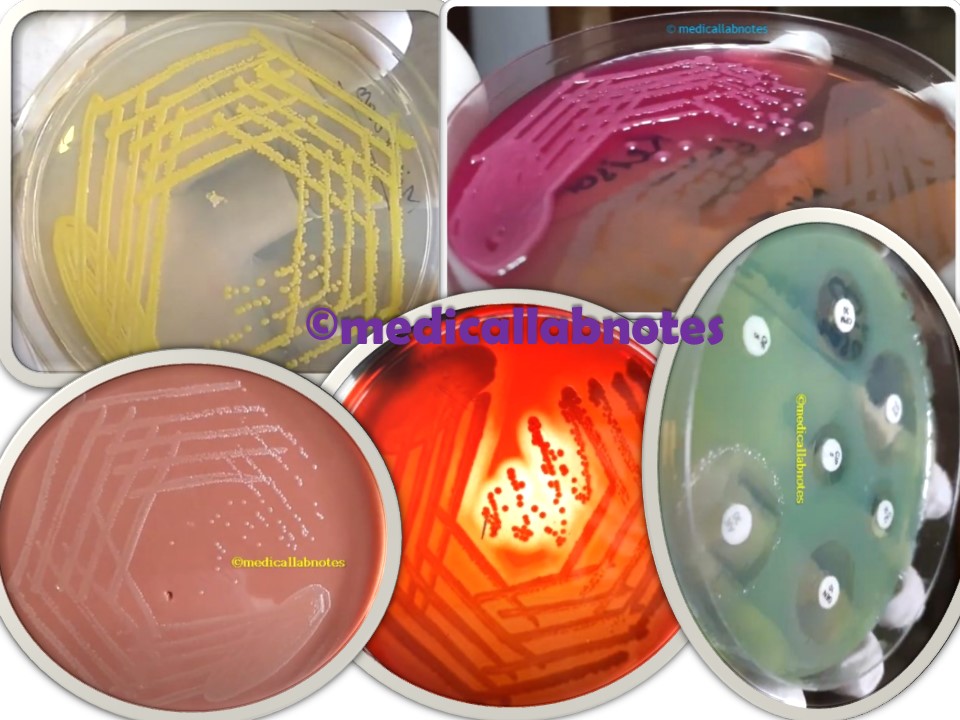
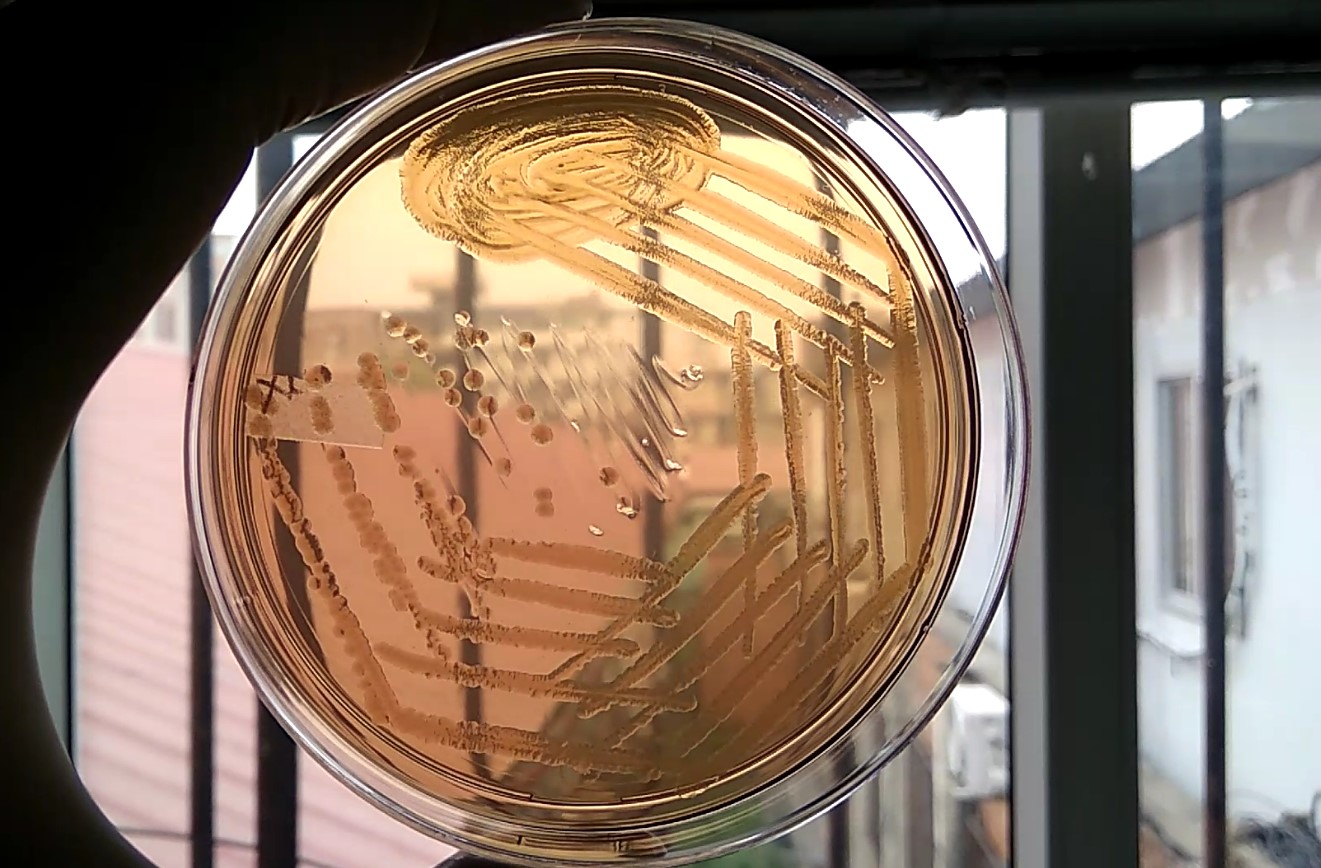
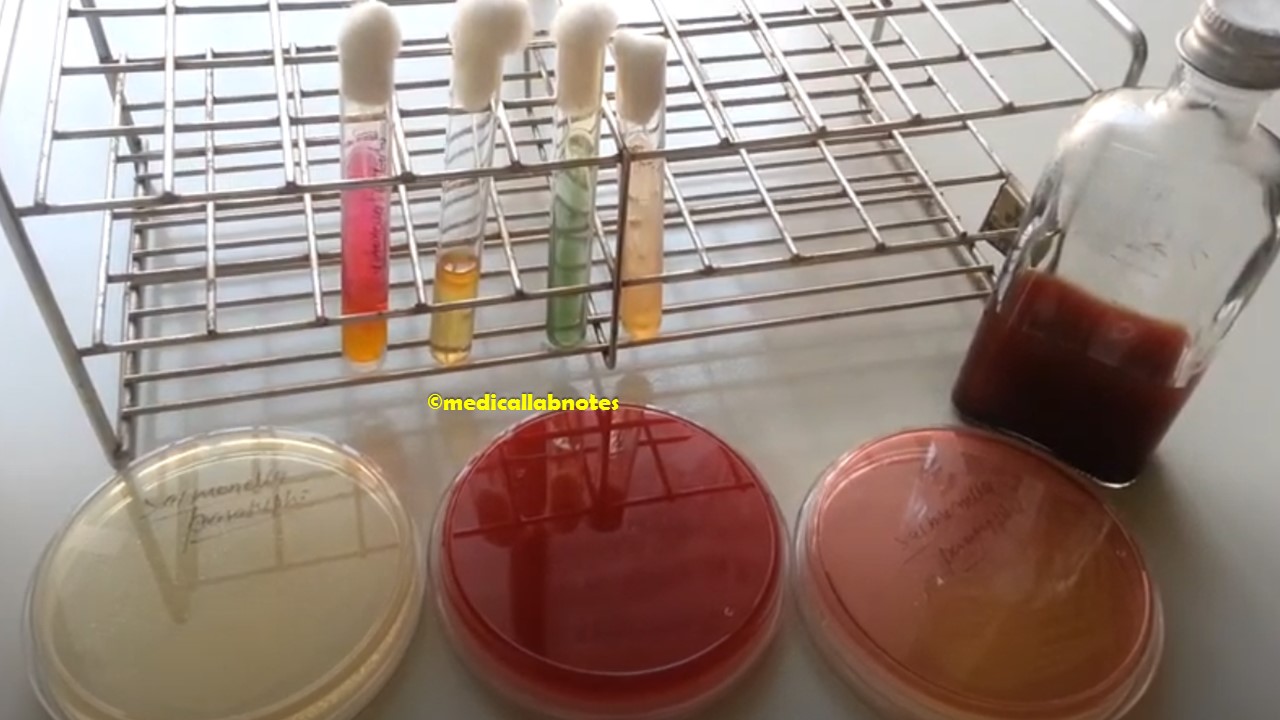
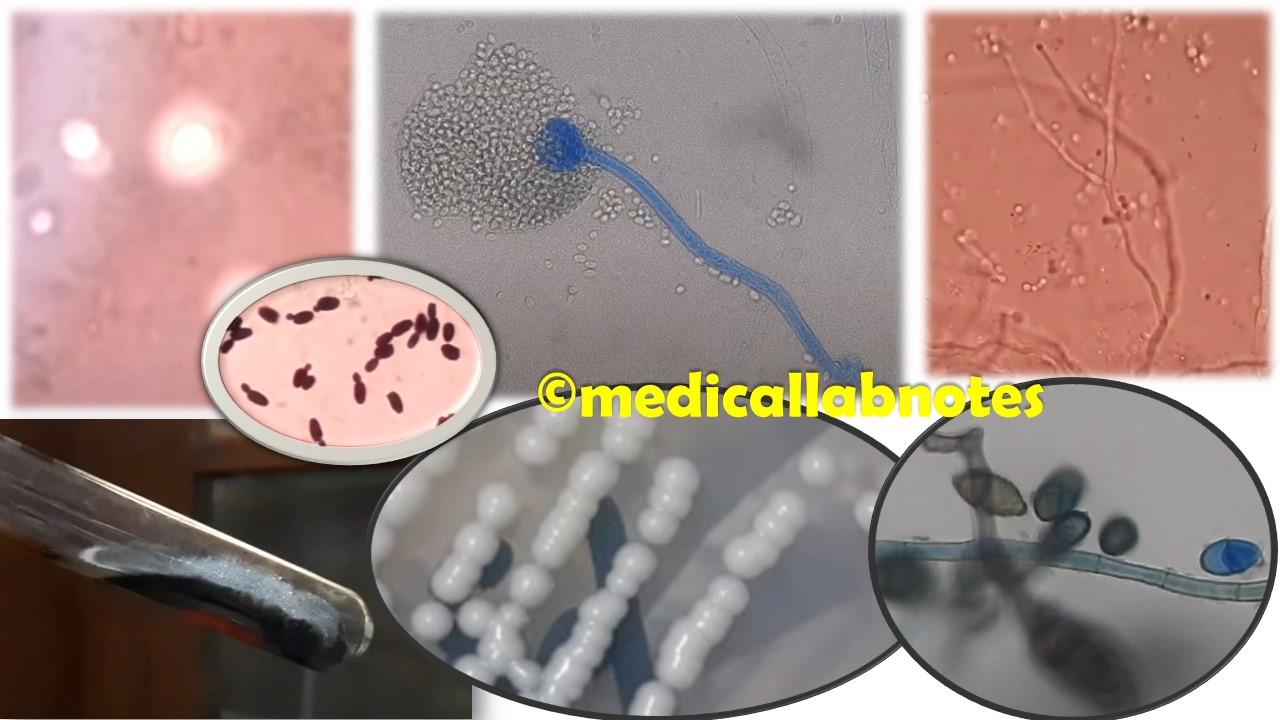
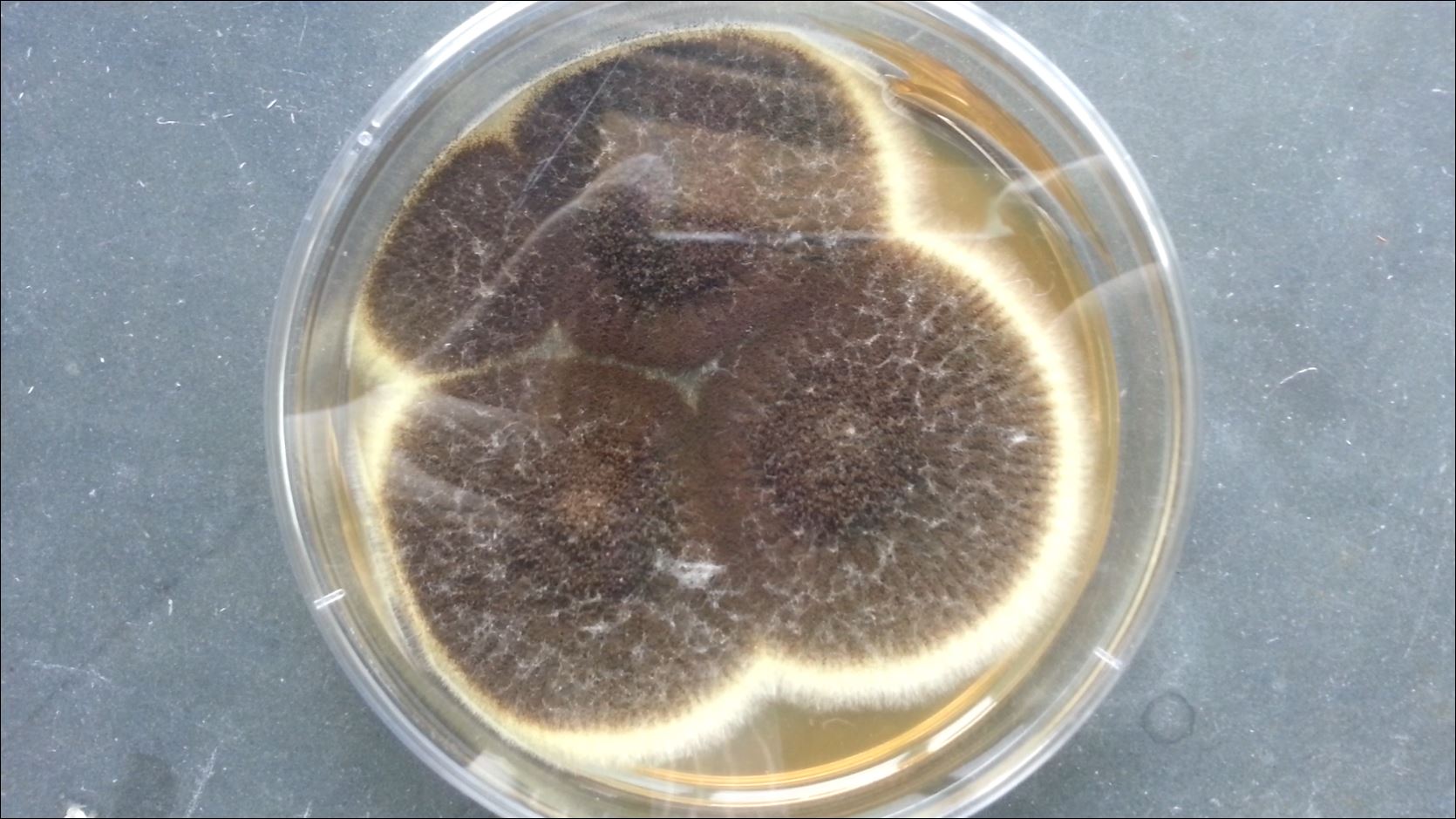
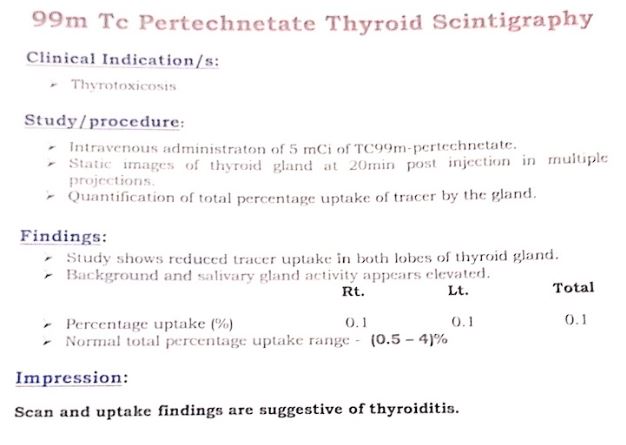
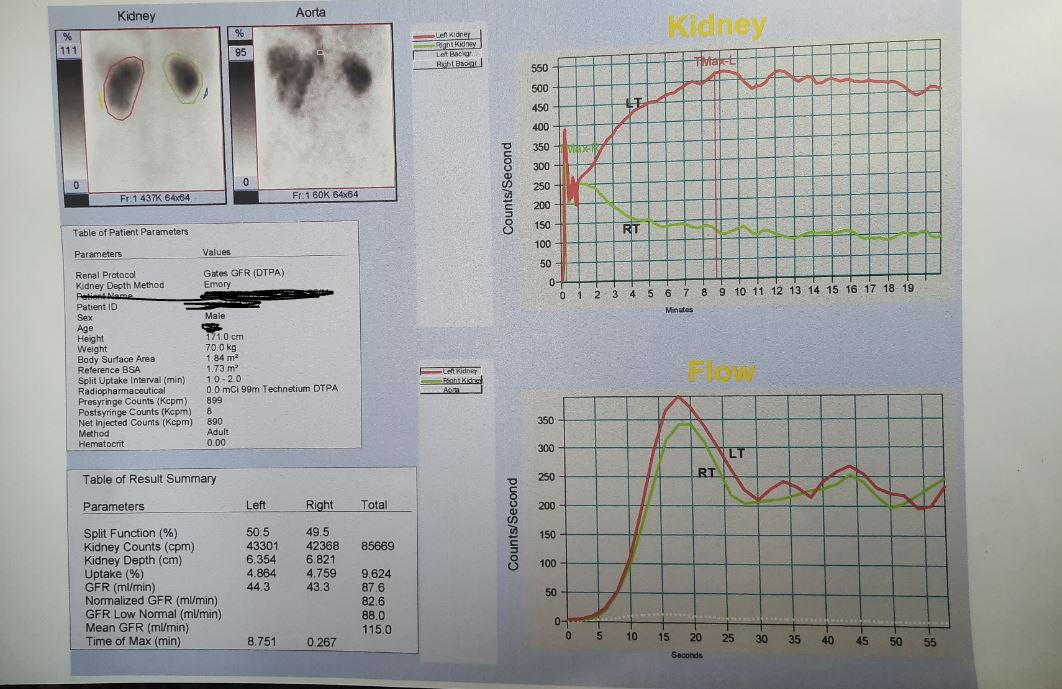
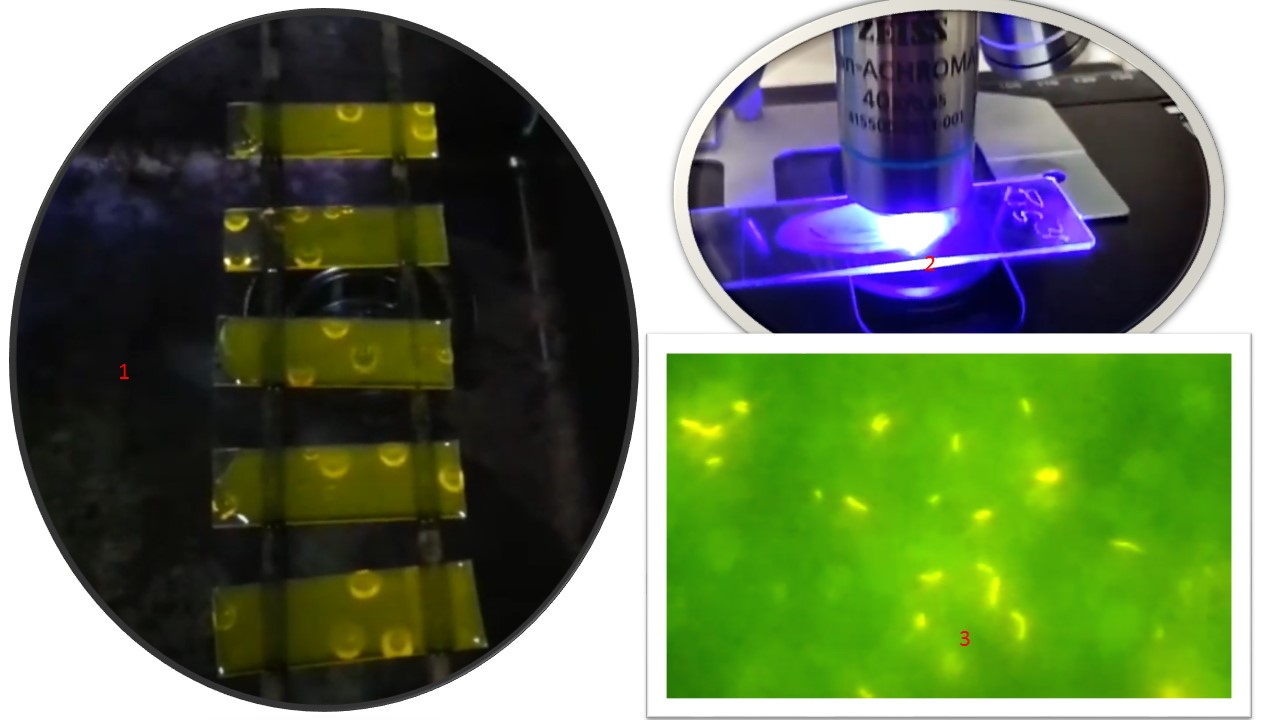
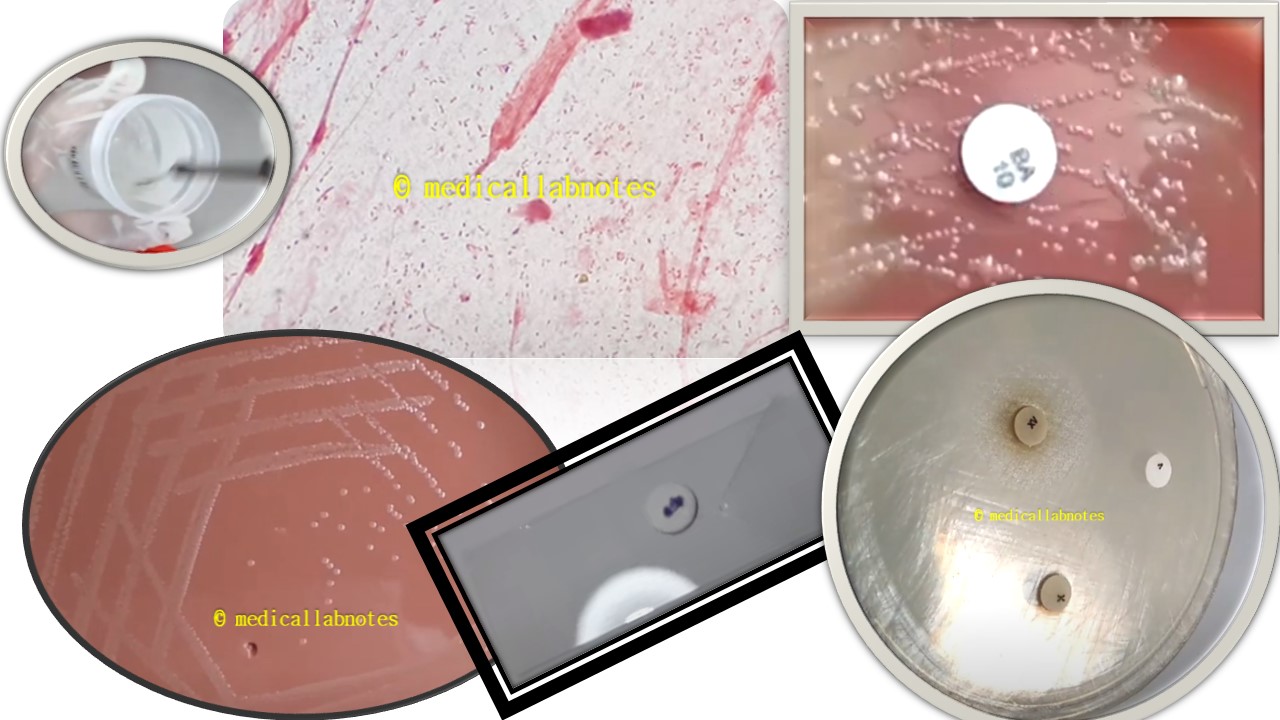
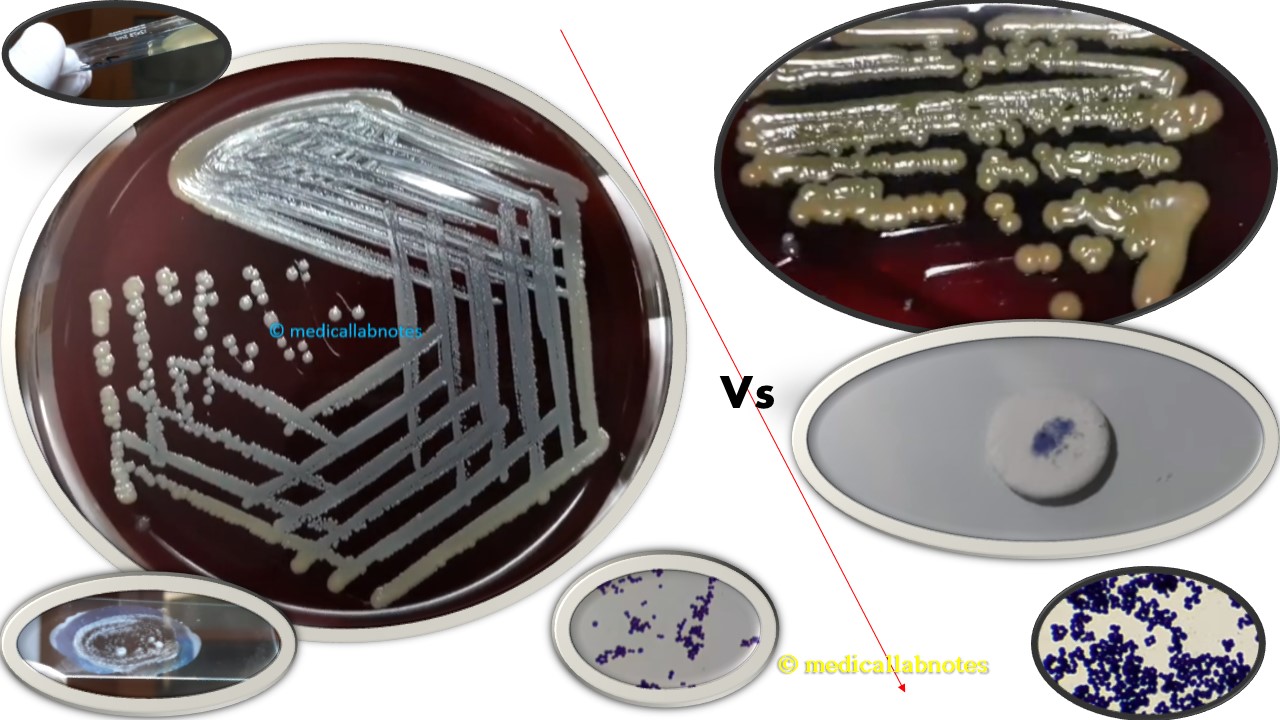
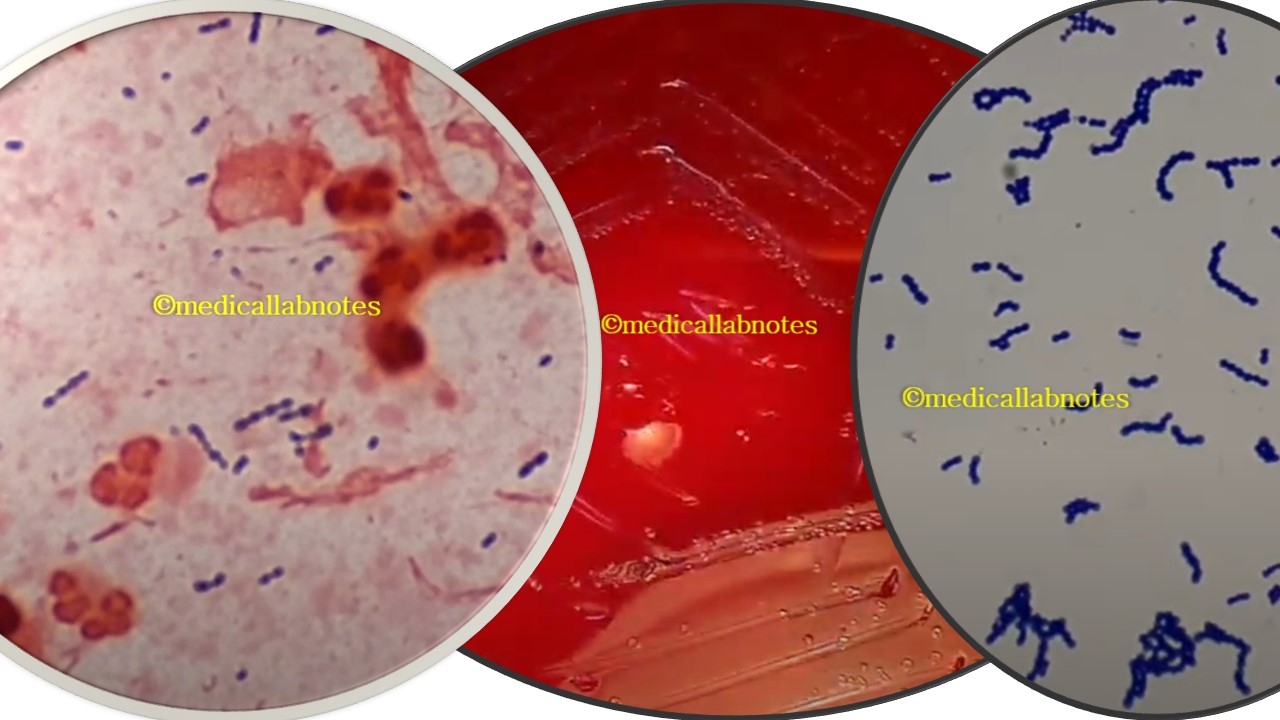
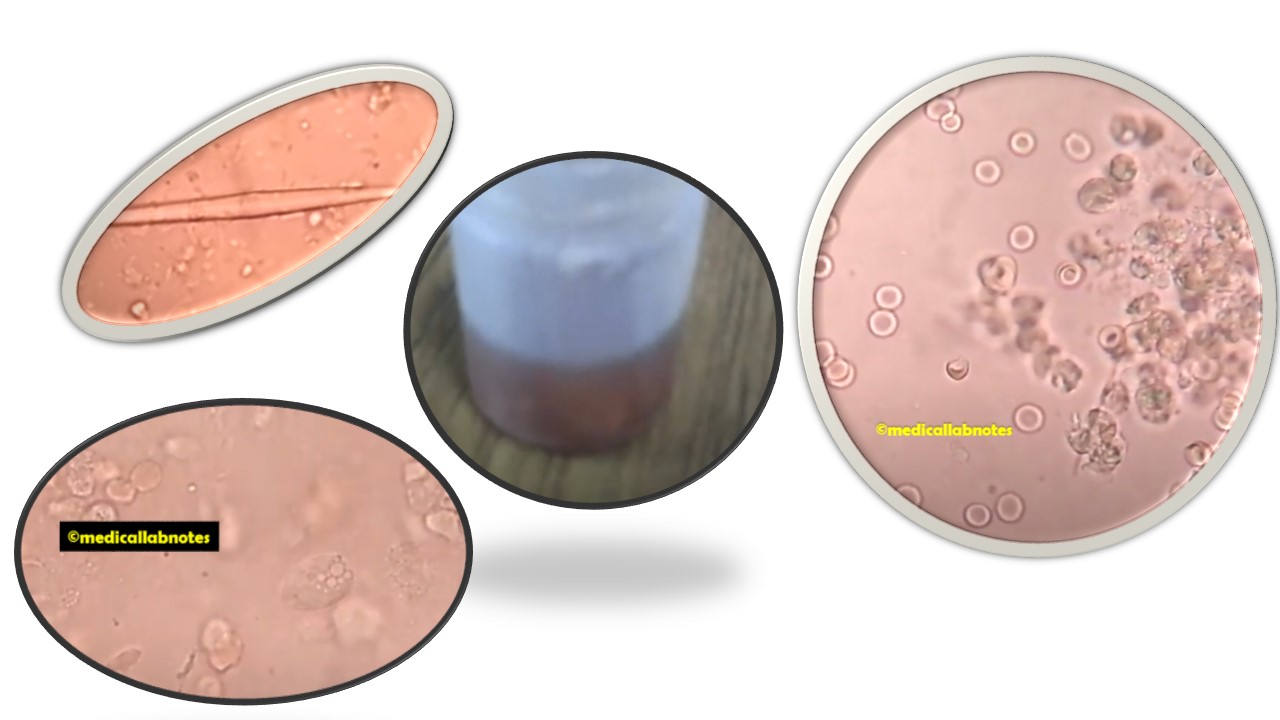
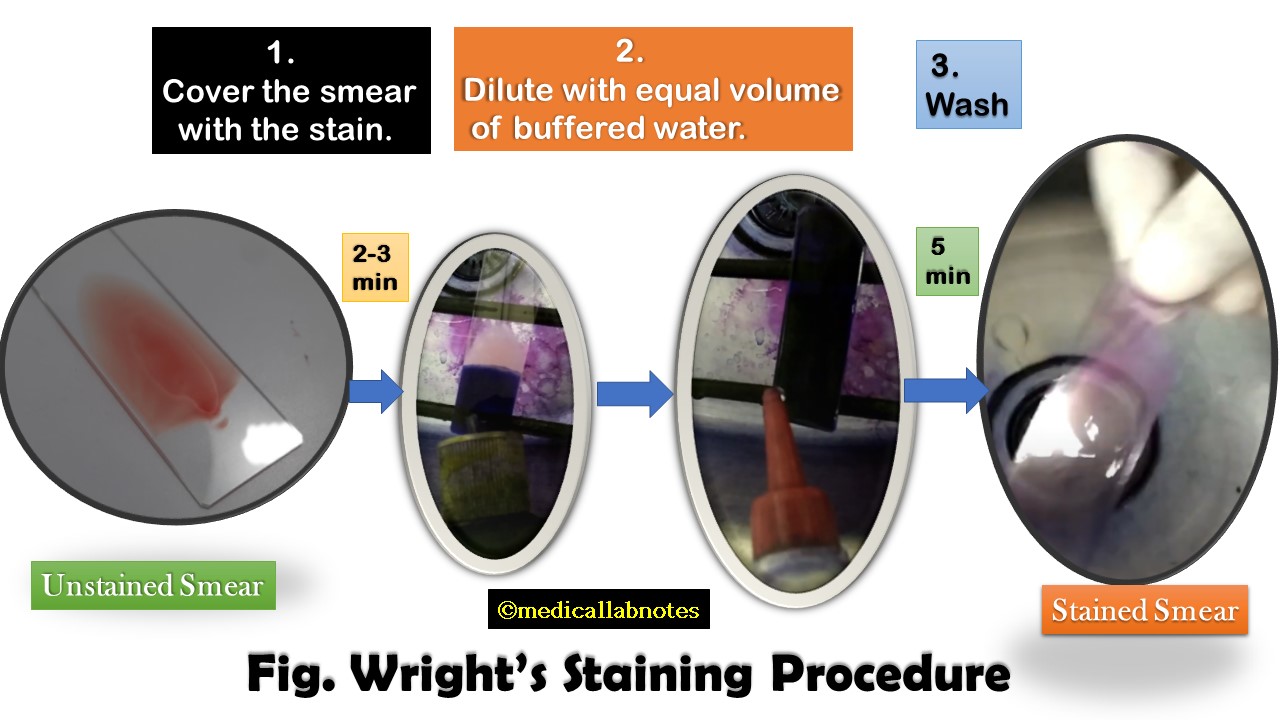
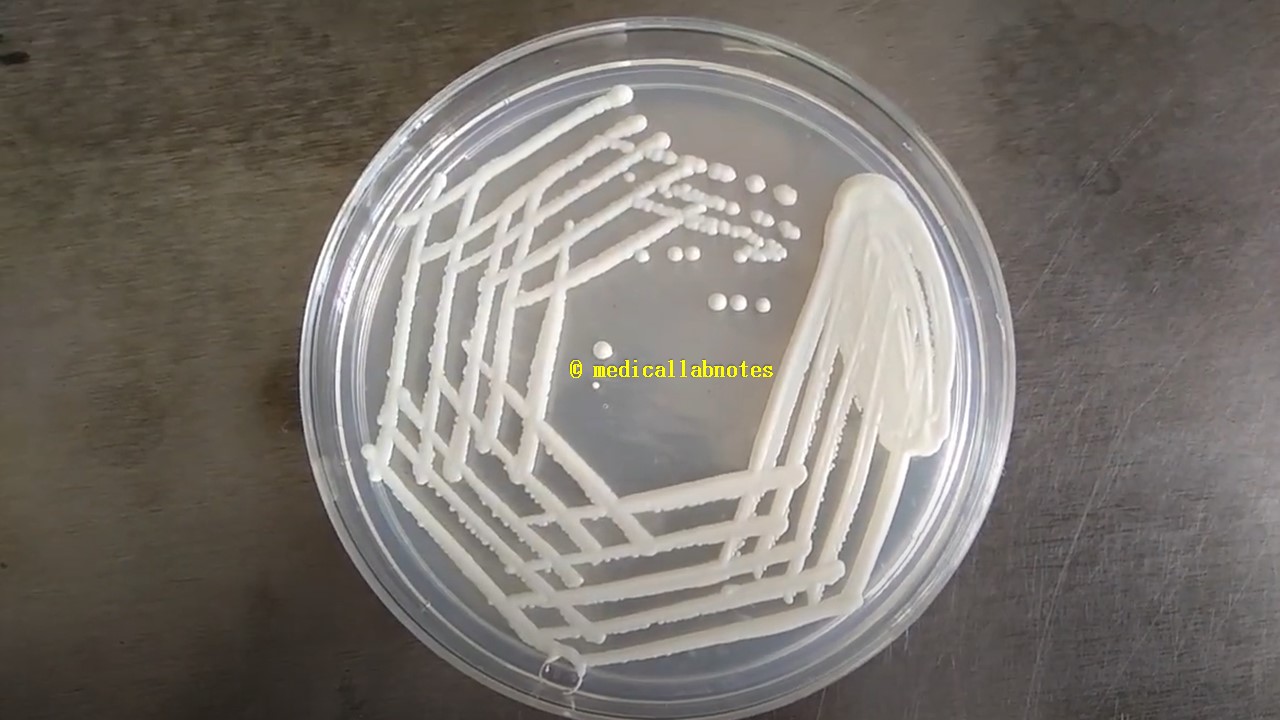
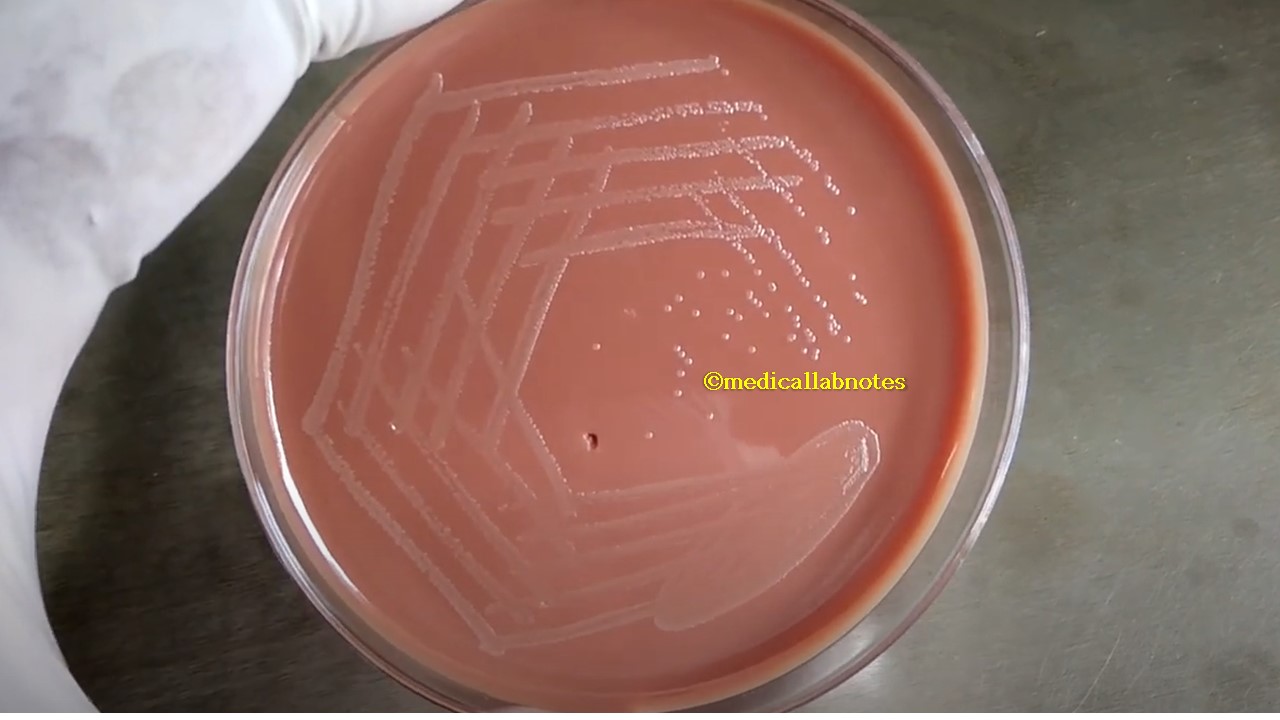
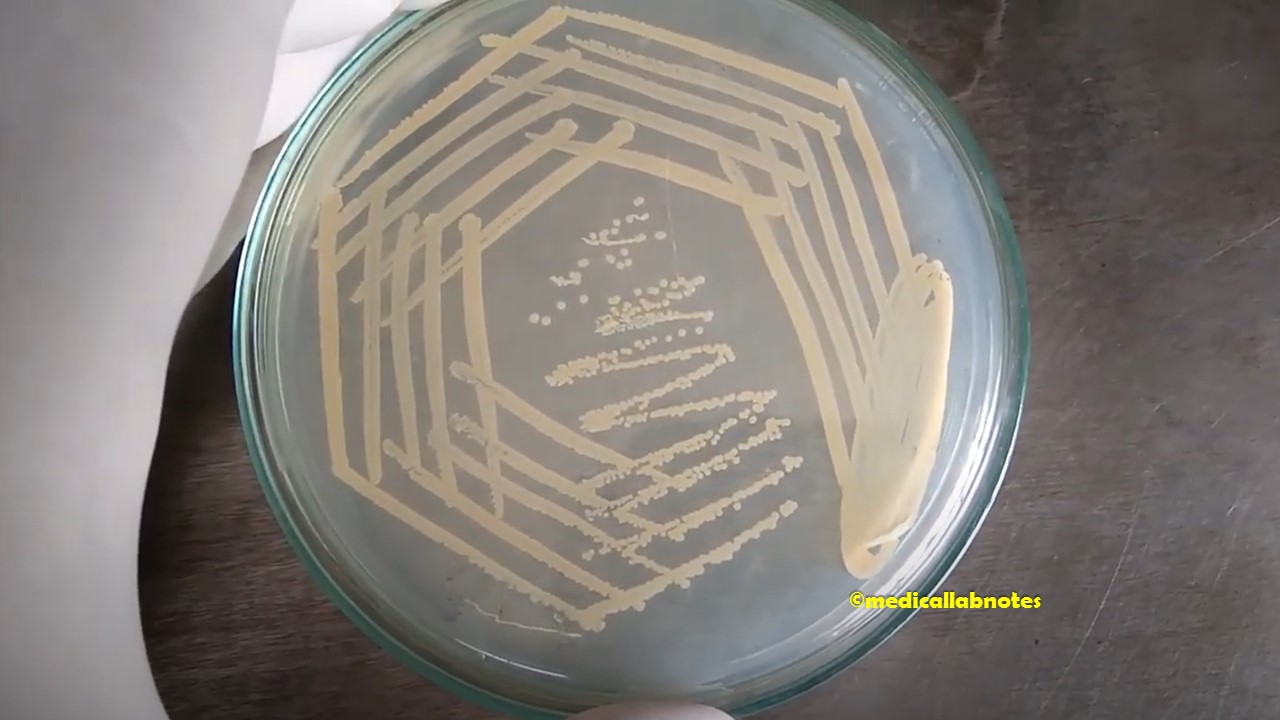
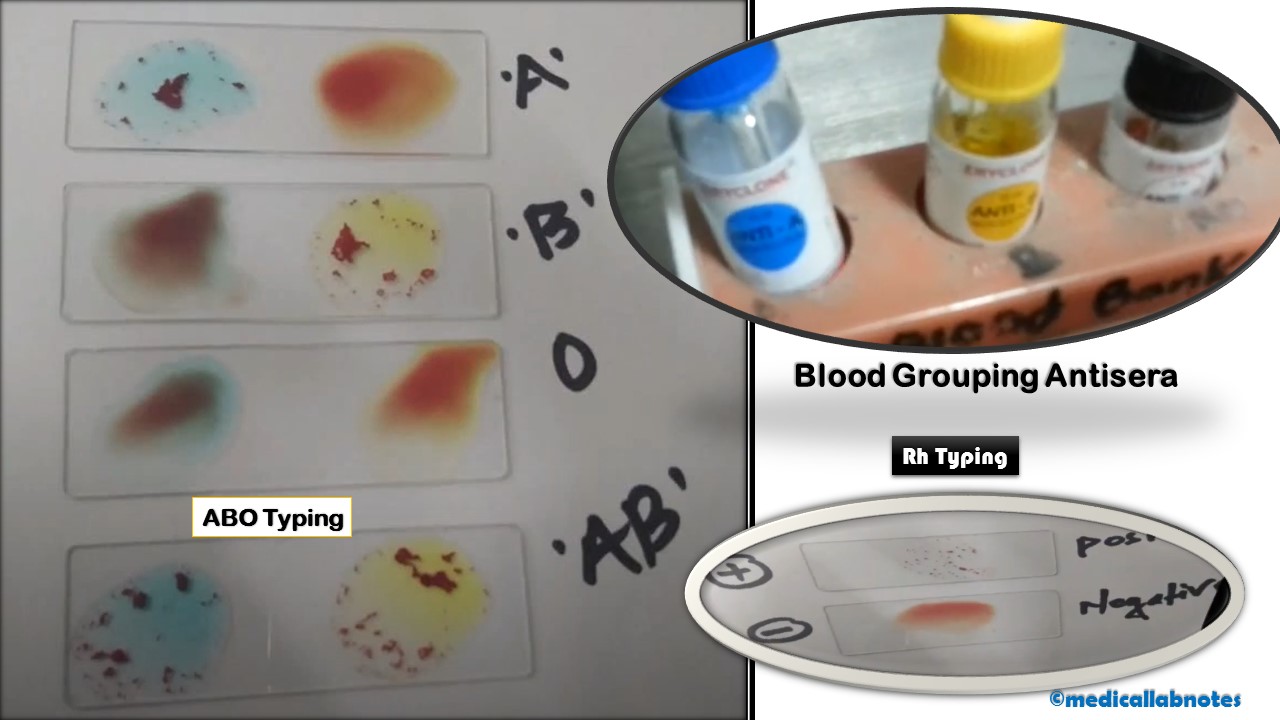
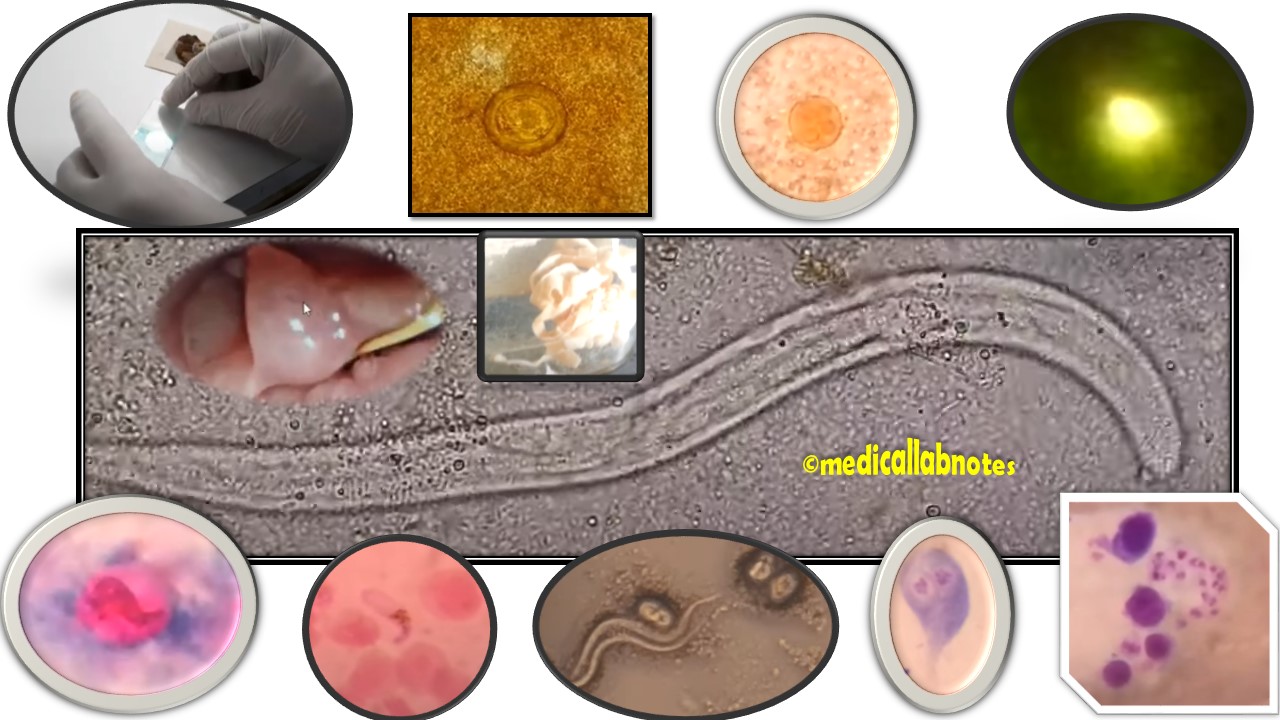
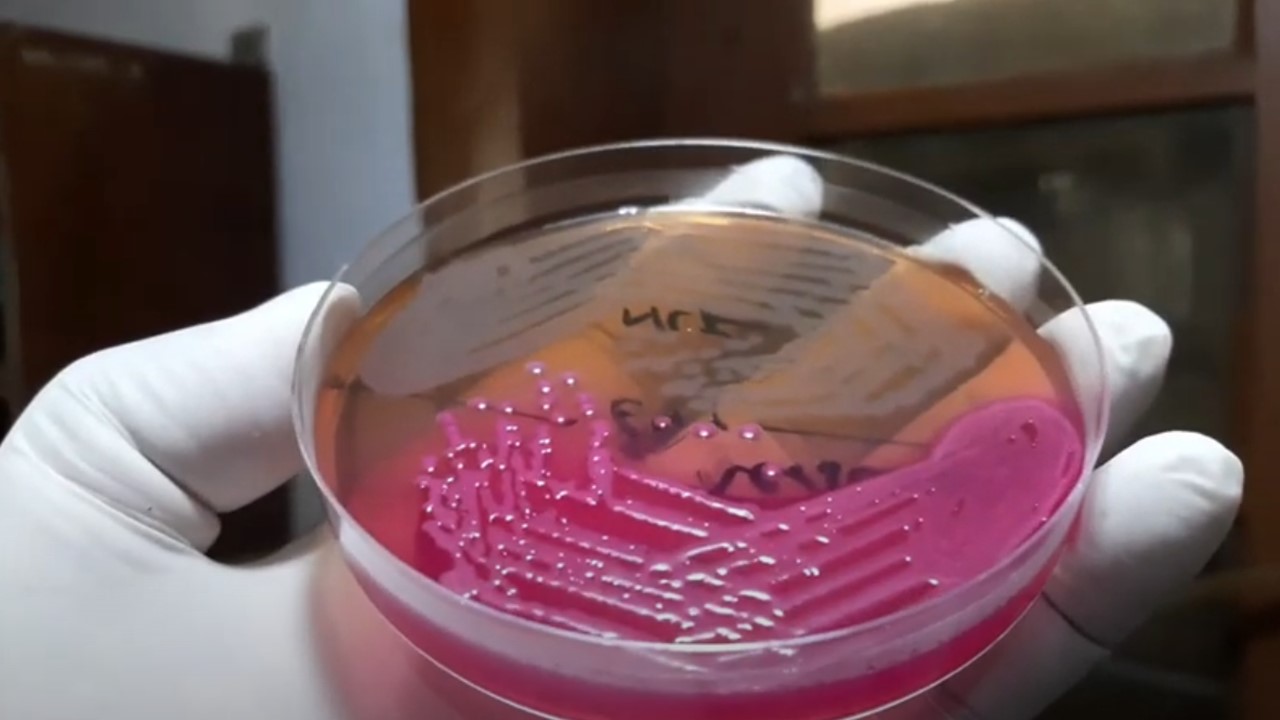
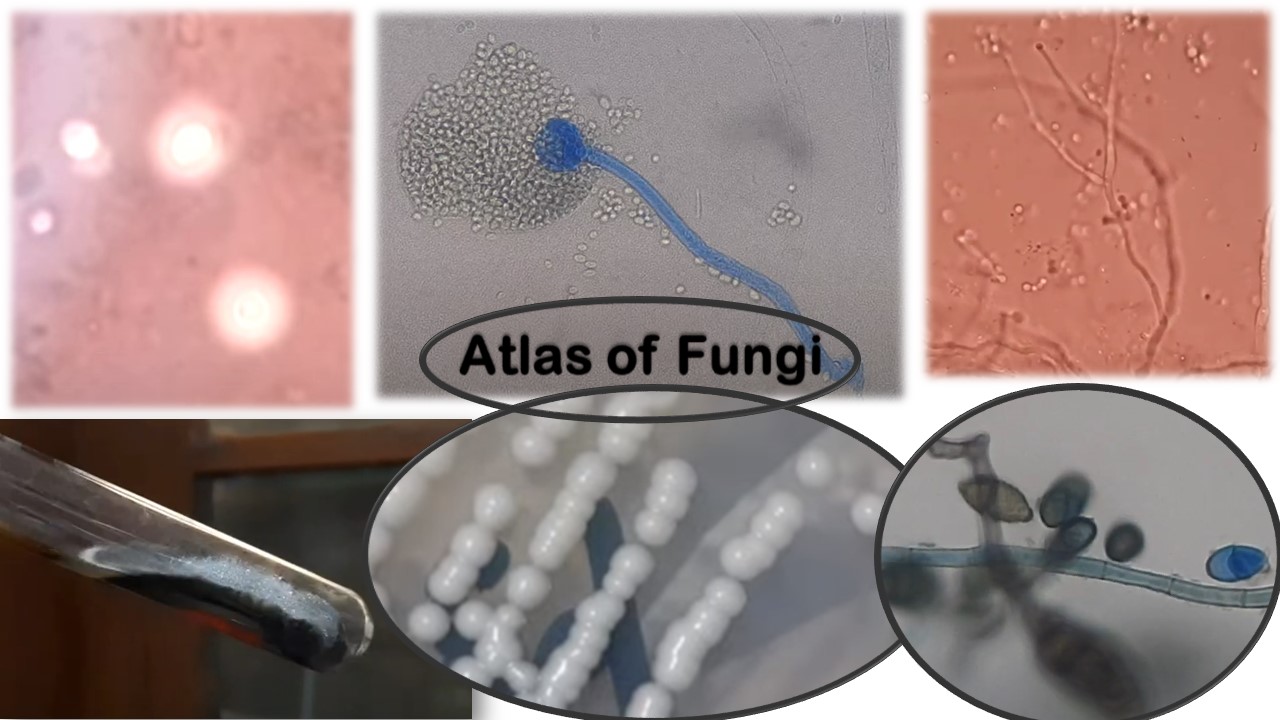
Penicillium cheresanum: Introduction, Morphology, Pathogenicity, Lab Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention, and Keynotes
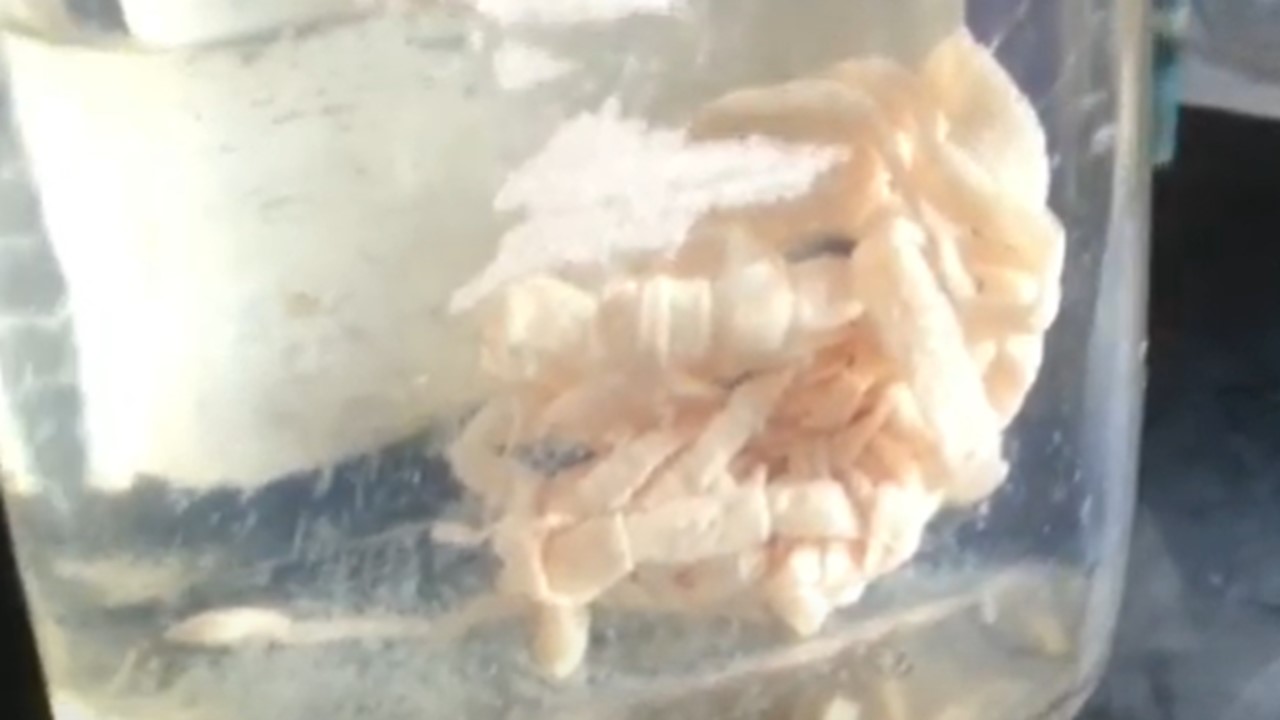
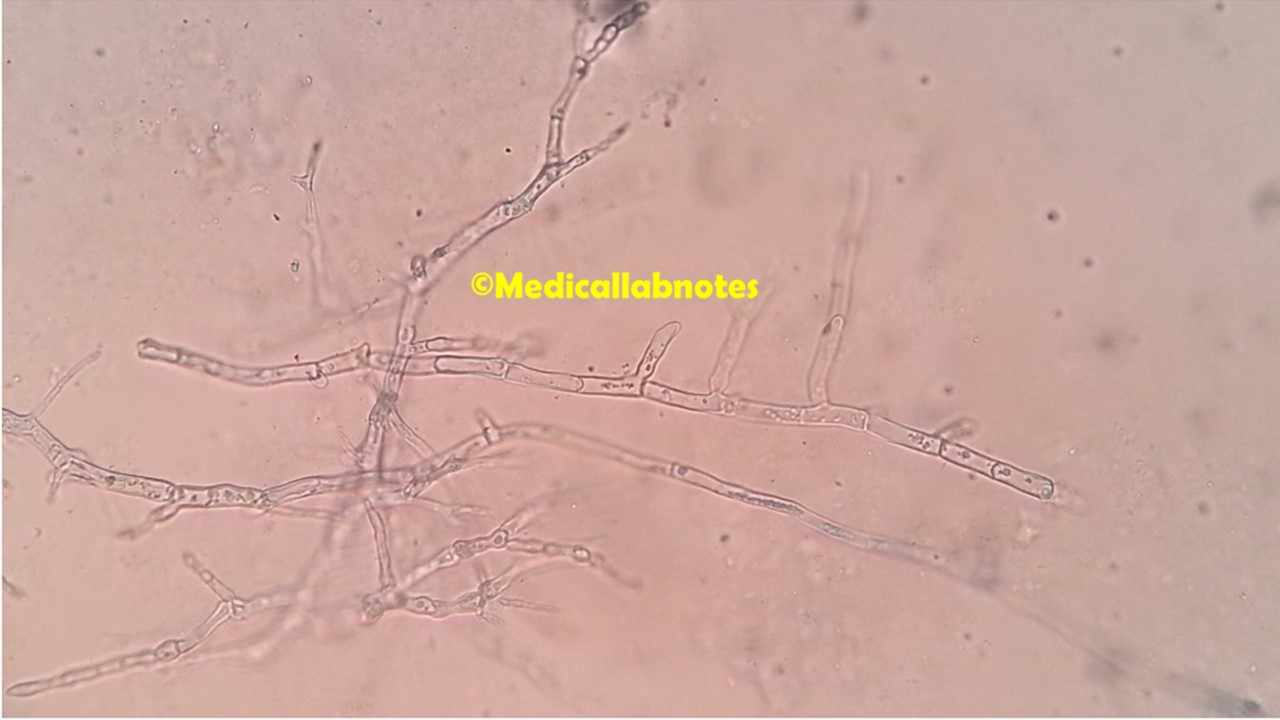
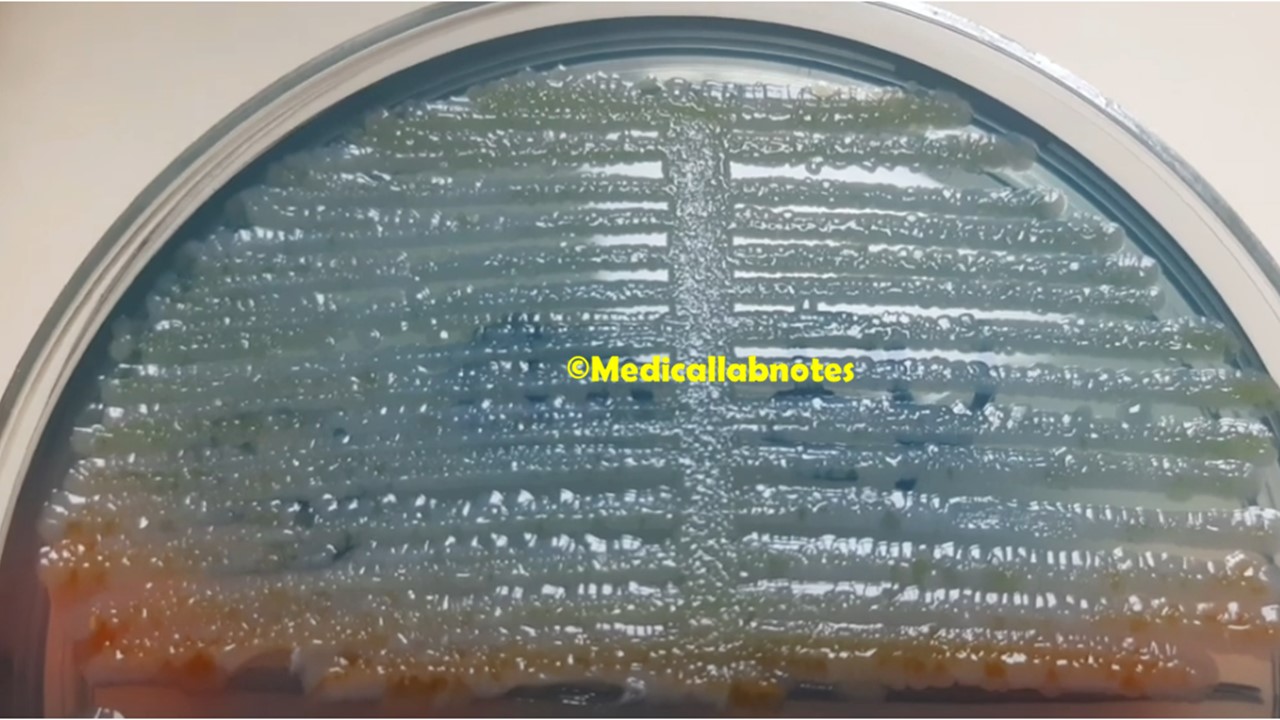
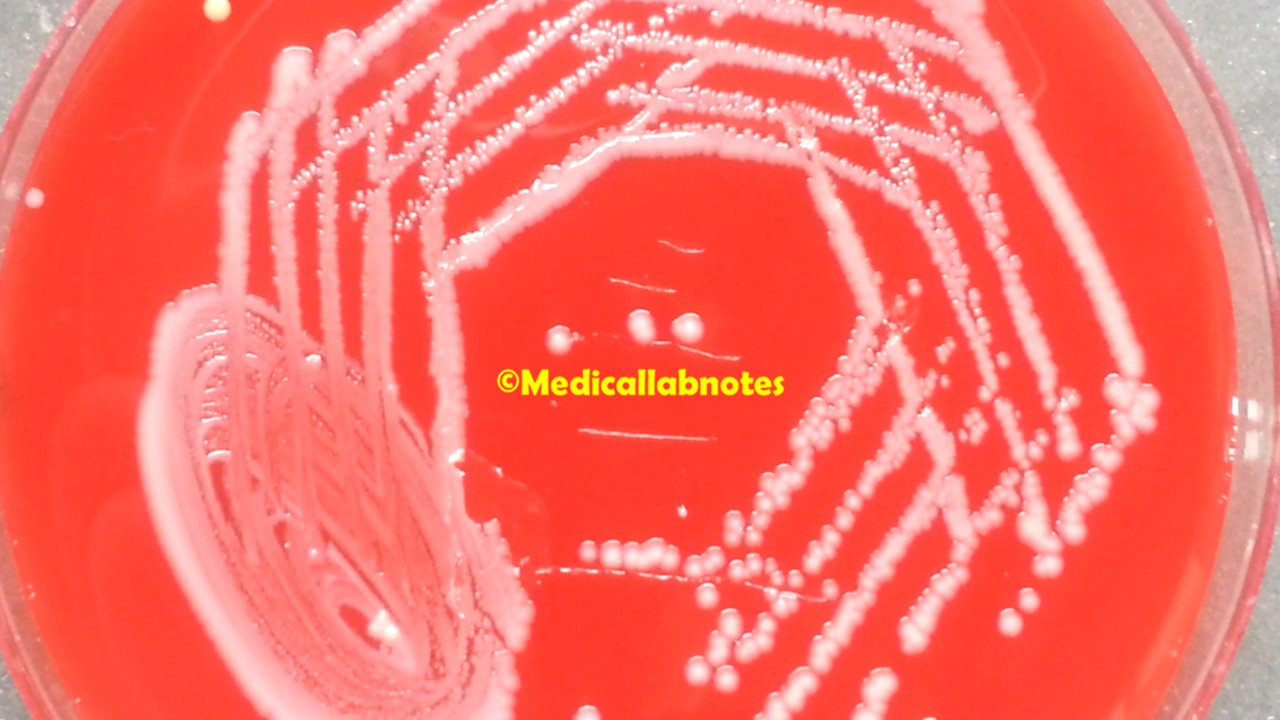
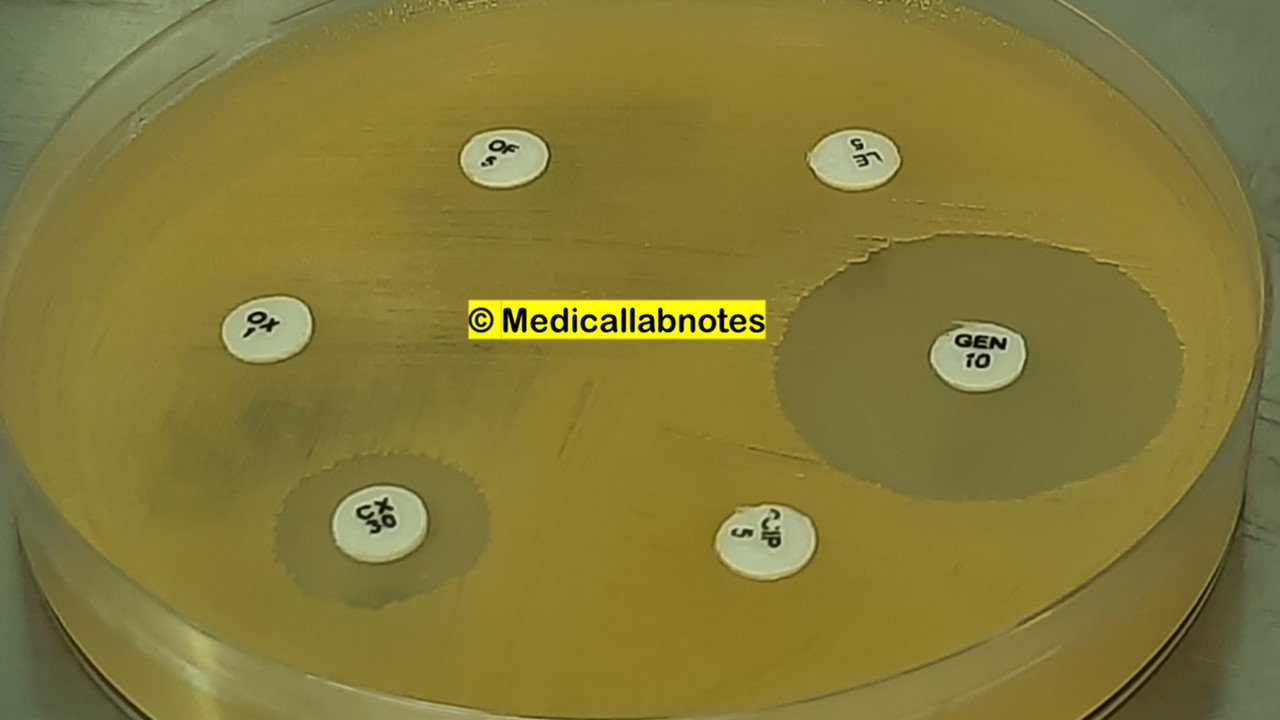
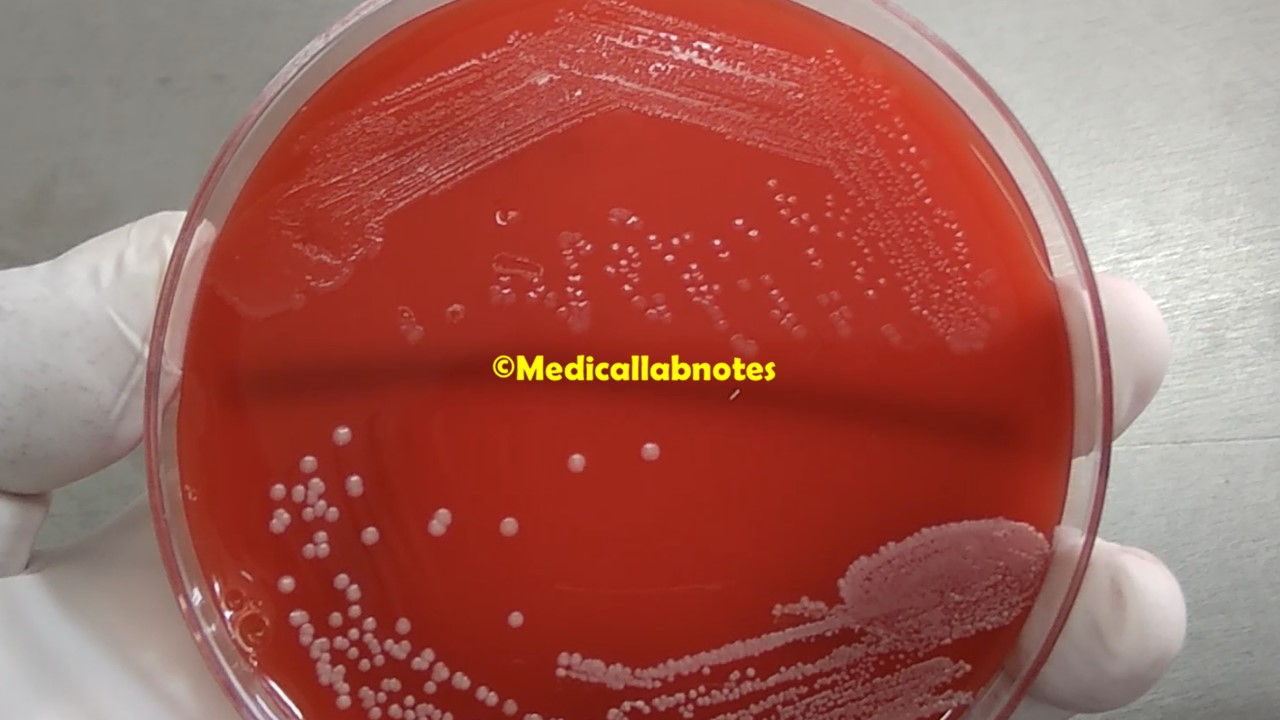
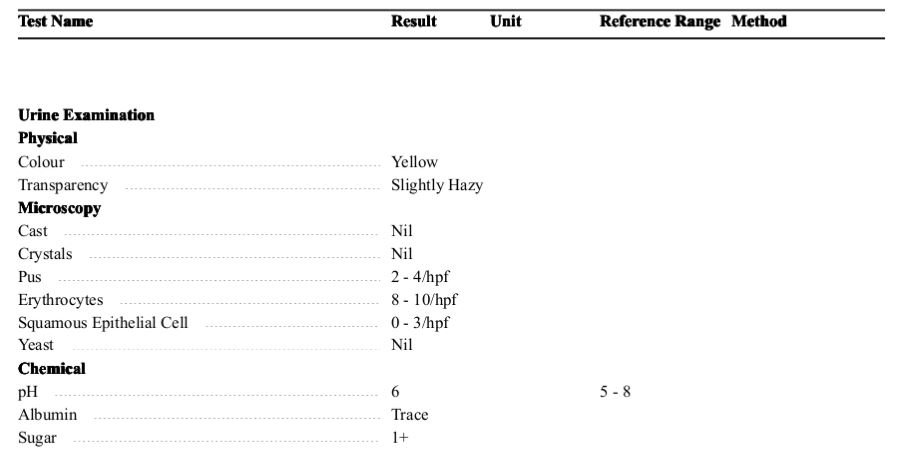
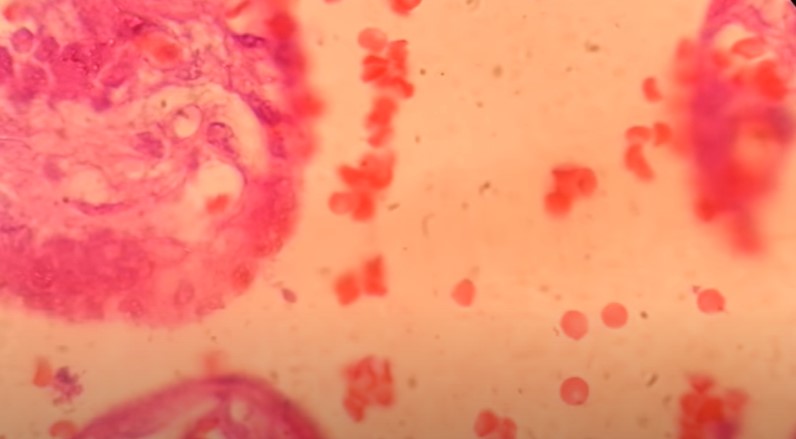
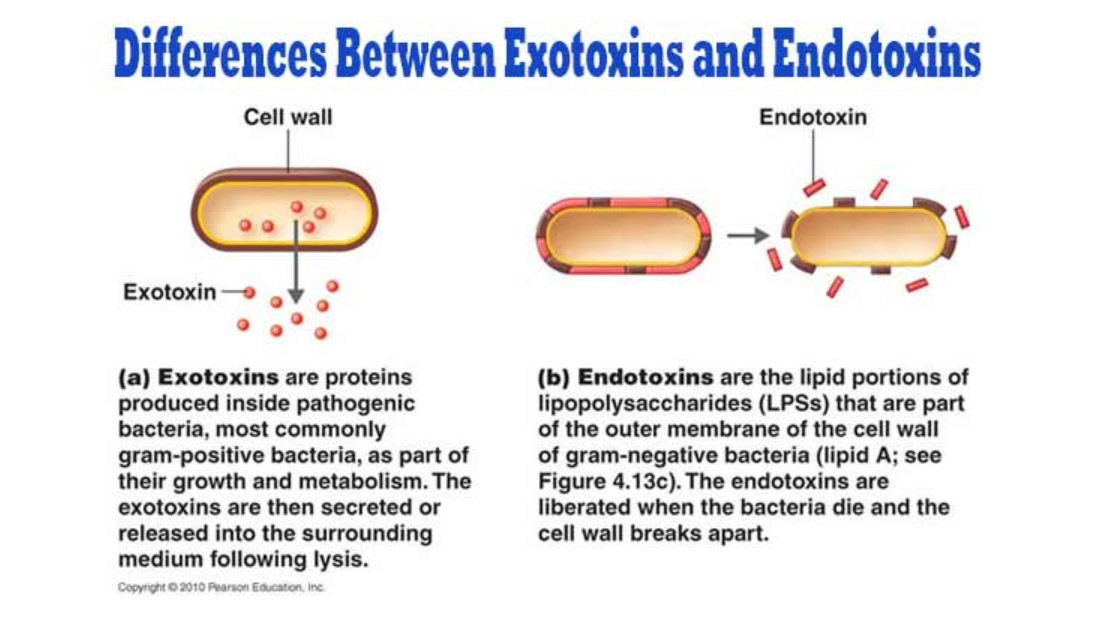
Introduction Penicillium cheresanum is a species of mold belonging to the genus Penicillium, commonly found in soil and decaying organic matter. Moreover, it thrives in a variety of environments, demonstrating its adaptability to different ecological conditions. In addition, this mold is known for producing secondary …