Introduction
Table of Contents
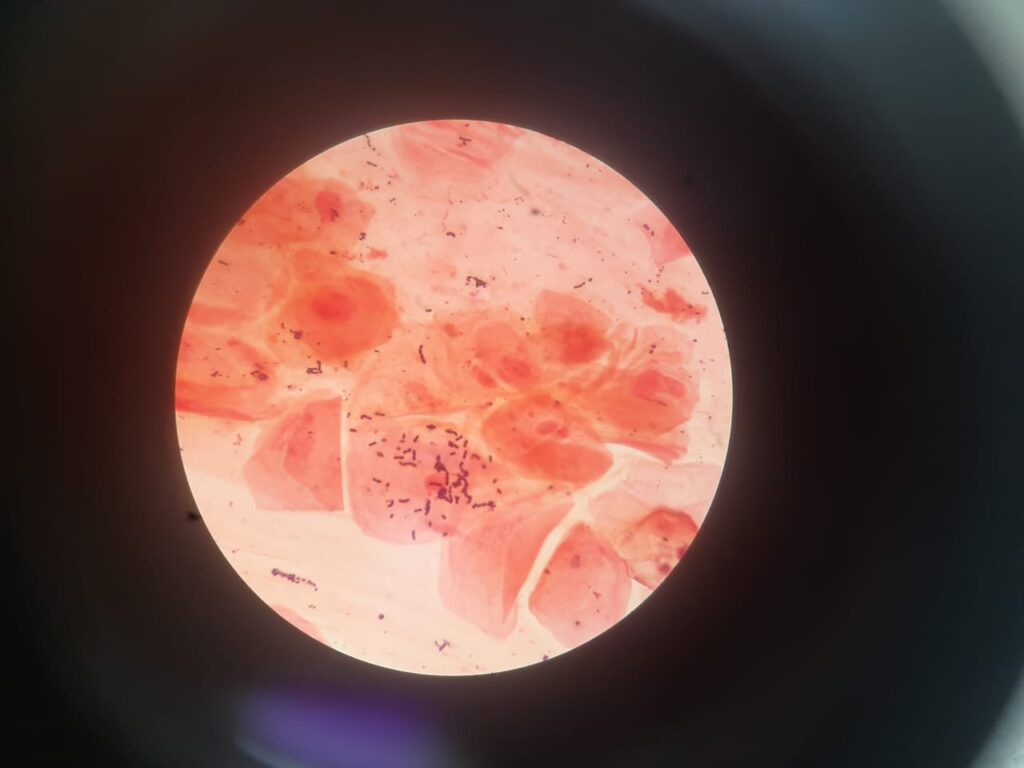
A throat swab Gram stain is a rapid, initial diagnostic test performed on specimens collected from the oropharynx or tonsillar region. It helps to identify bacterial flora, pathogens, and inflammatory response. While culture and molecular methods provide definitive diagnosis, Gram staining offers early guidance in suspected cases of bacterial pharyngitis, tonsillitis, diphtheria, gonococcal pharyngitis, or candidiasis.
Report – Interpretation
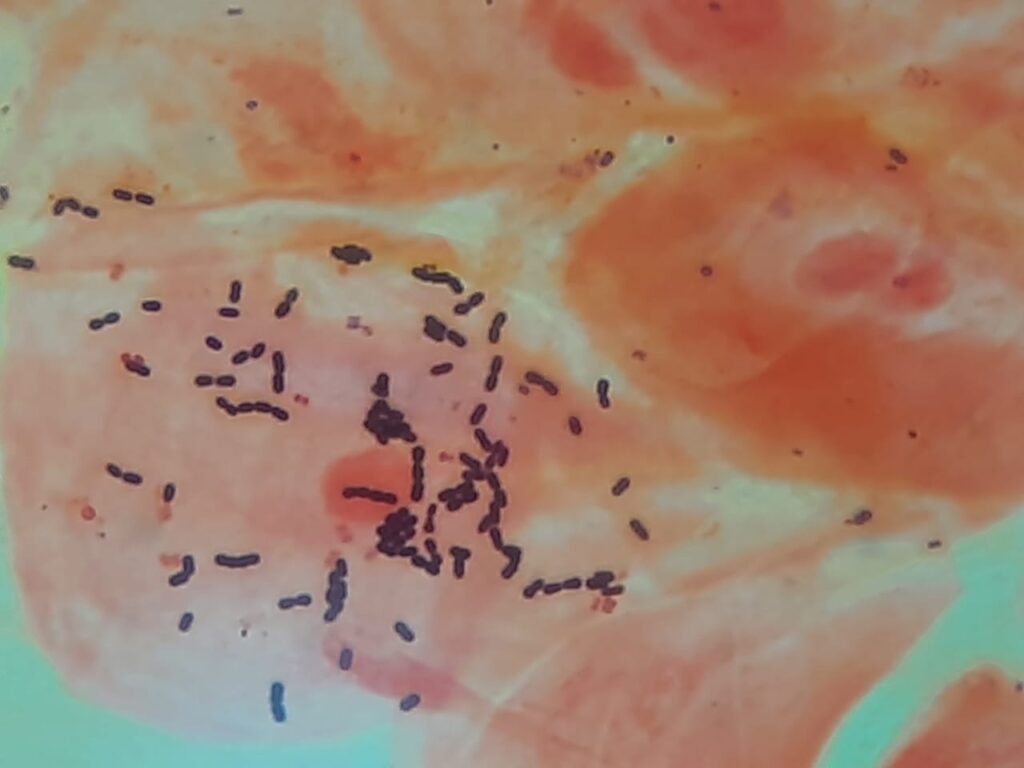
- Normal Findings (Commensals):
- Mixed flora of Gram-positive cocci (streptococci, staphylococci) and Gram-negative cocci/rods.
- Few epithelial cells.
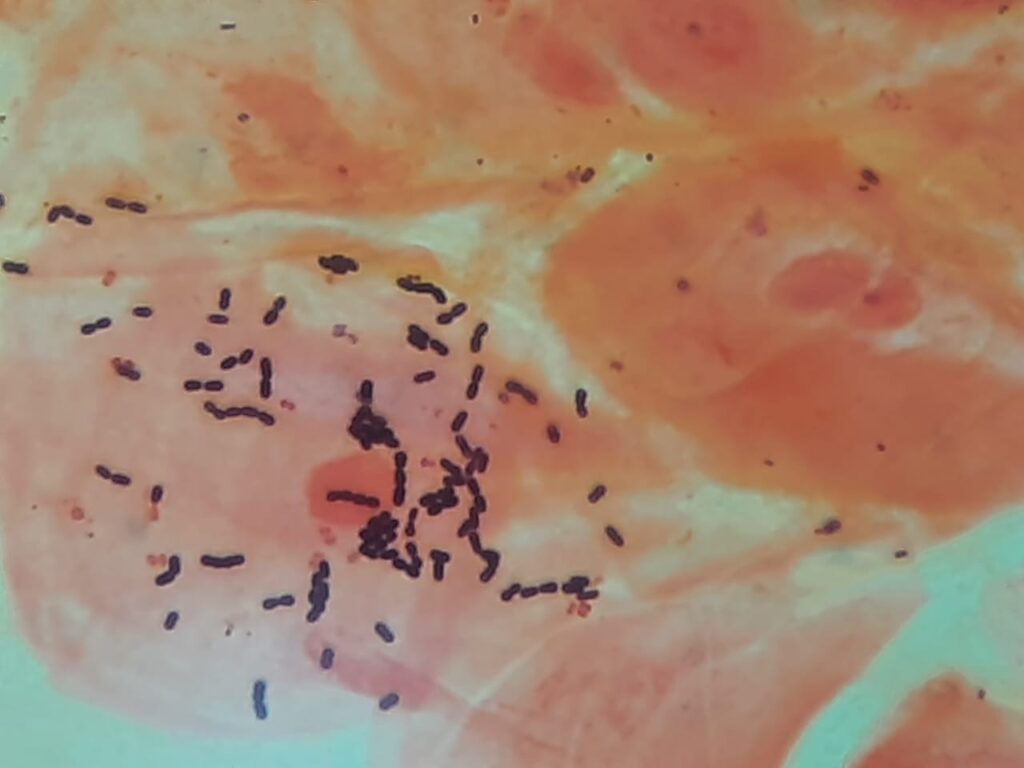
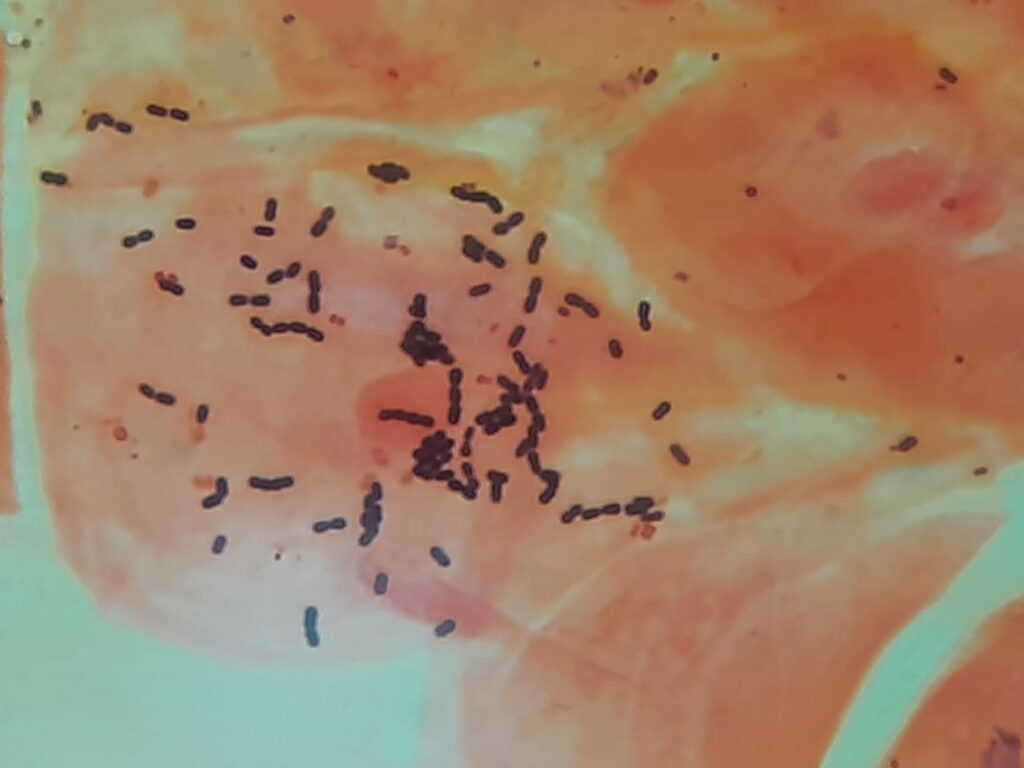
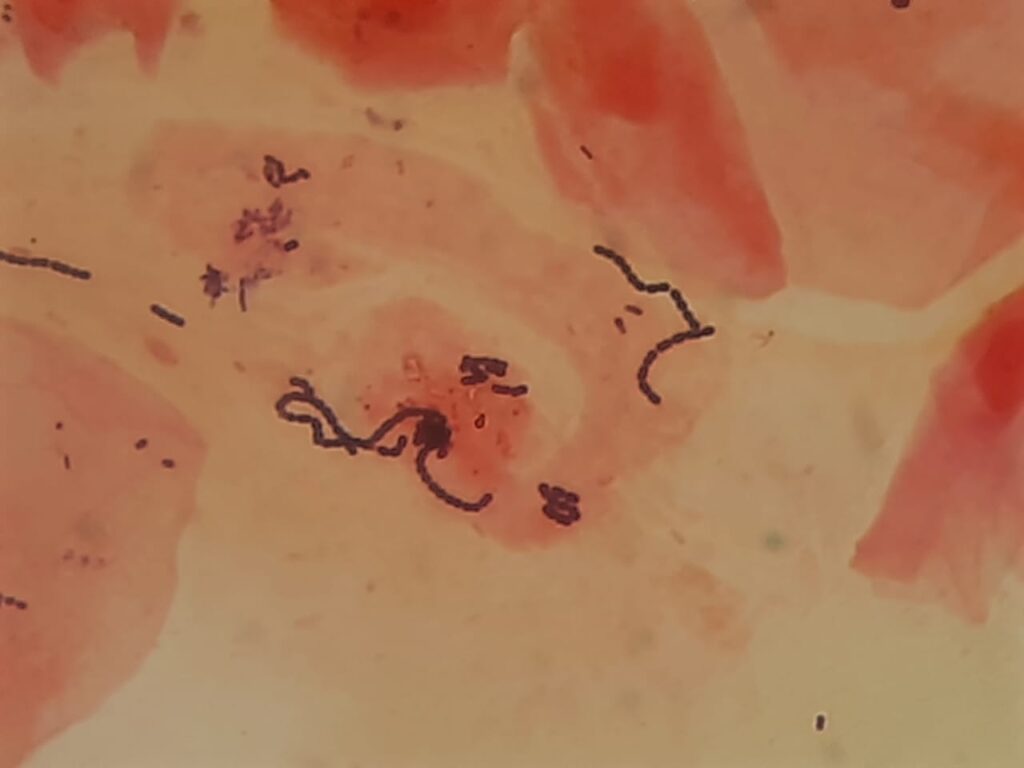
- Abnormal Findings / Pathogens:
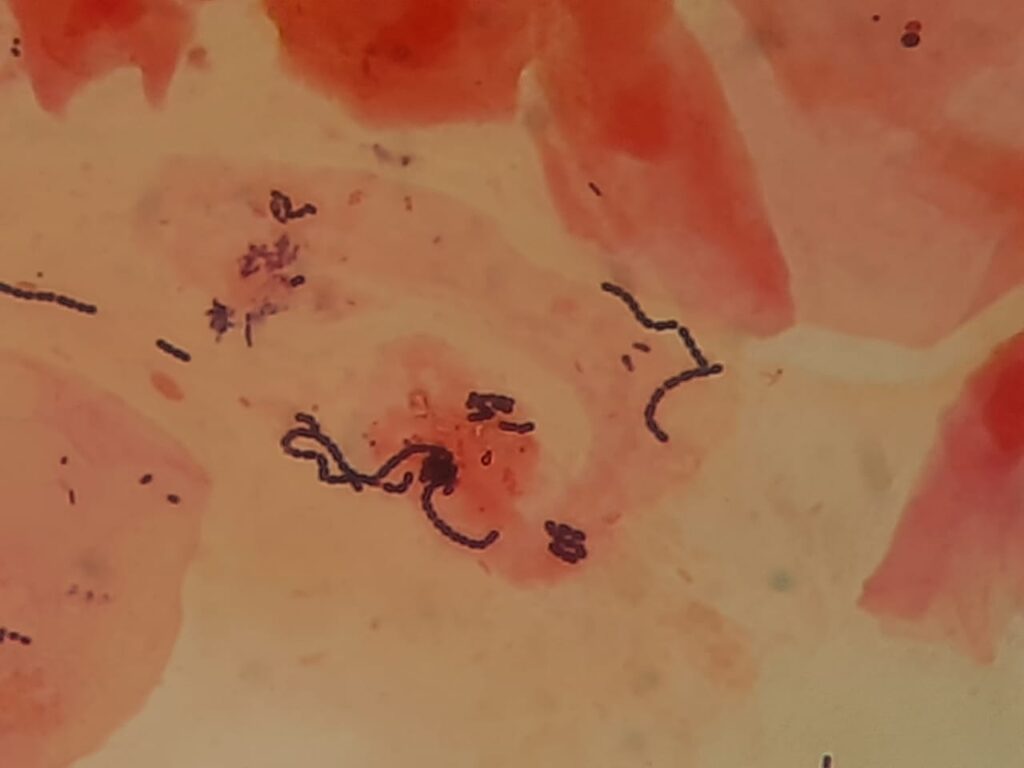
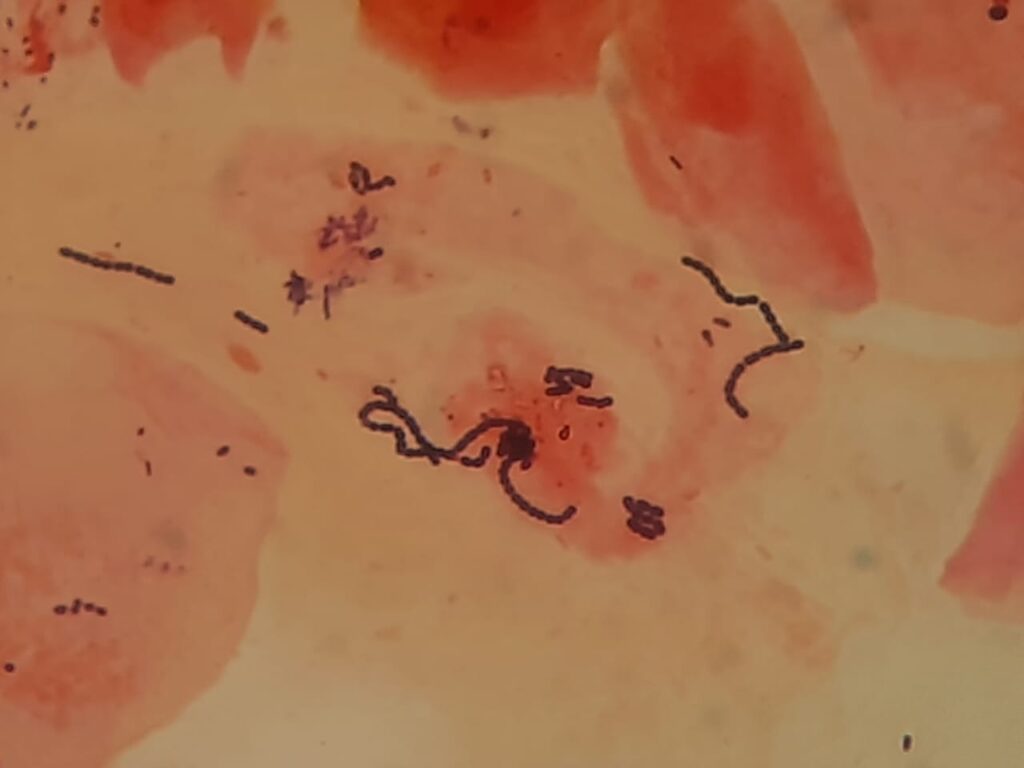
- Gram-positive cocci in chains: Suggests Streptococcus pyogenes (Group A Strep, common cause of strep throat).
- Gram-positive bacilli (club-shaped, arranged in palisades): Suggestive of Corynebacterium diphtheriae.
- Gram-negative diplococci (intracellular): Possible Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
- Budding yeast with pseudohyphae: Indicates Candida albicans infection (oral thrush).
- Excessive neutrophils: Suggest acute bacterial infection.
- Excessive epithelial cells: Suggest poor-quality specimen (more saliva than throat exudate).
Clinical Significance
- Provides early presumptive evidence of bacterial vs fungal throat infection.
- Guides clinicians to initiate empirical therapy before culture results.
- Helps differentiate commensals from pathogenic dominance.
- Critical for early detection of high-risk pathogens like Corynebacterium diphtheriae and Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
- Plays a role in antimicrobial stewardship by preventing unnecessary antibiotic use when only commensal flora is seen.
Keynotes
- Throat swab Gram stain is a quick, inexpensive, and valuable screening tool.
- Presence of predominant organisms with inflammatory cells supports infection, whereas a mixed flora without neutrophils may represent colonization.
- Always correlate with culture, antigen detection, or PCR for definitive diagnosis.
- Proper specimen collection technique (avoiding contamination with saliva) is essential for reliable results.
- Particularly useful in suspected streptococcal pharyngitis, diphtheria, gonococcal pharyngitis, and candidiasis.
Further Readings
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/305562549_Significance_of_direct_Gram_stained_smear_examination_in_sore_throat
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK562156/
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/22612-gram-stain
- https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/2093371-overview
- https://www.apollohospitals.com/diagnostics-investigations/gram-stain-test
- https://medlineplus.gov/lab-tests/gram-stain/
- http://maadi-clinical.byethost8.com/d/topic.htm?path=approach-to-gram-stain-and-culture-results-in-the-microbiology-laboratory
- https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/2121004-overview
- https://www.healthline.com/health/throat-swab-culture
- https://www.testing.com/tests/gram-stain/
- https://www.droracle.ai/articles/46726/what-do-gram-negative-bacilli-in-throat-culture-show-
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7734209/
