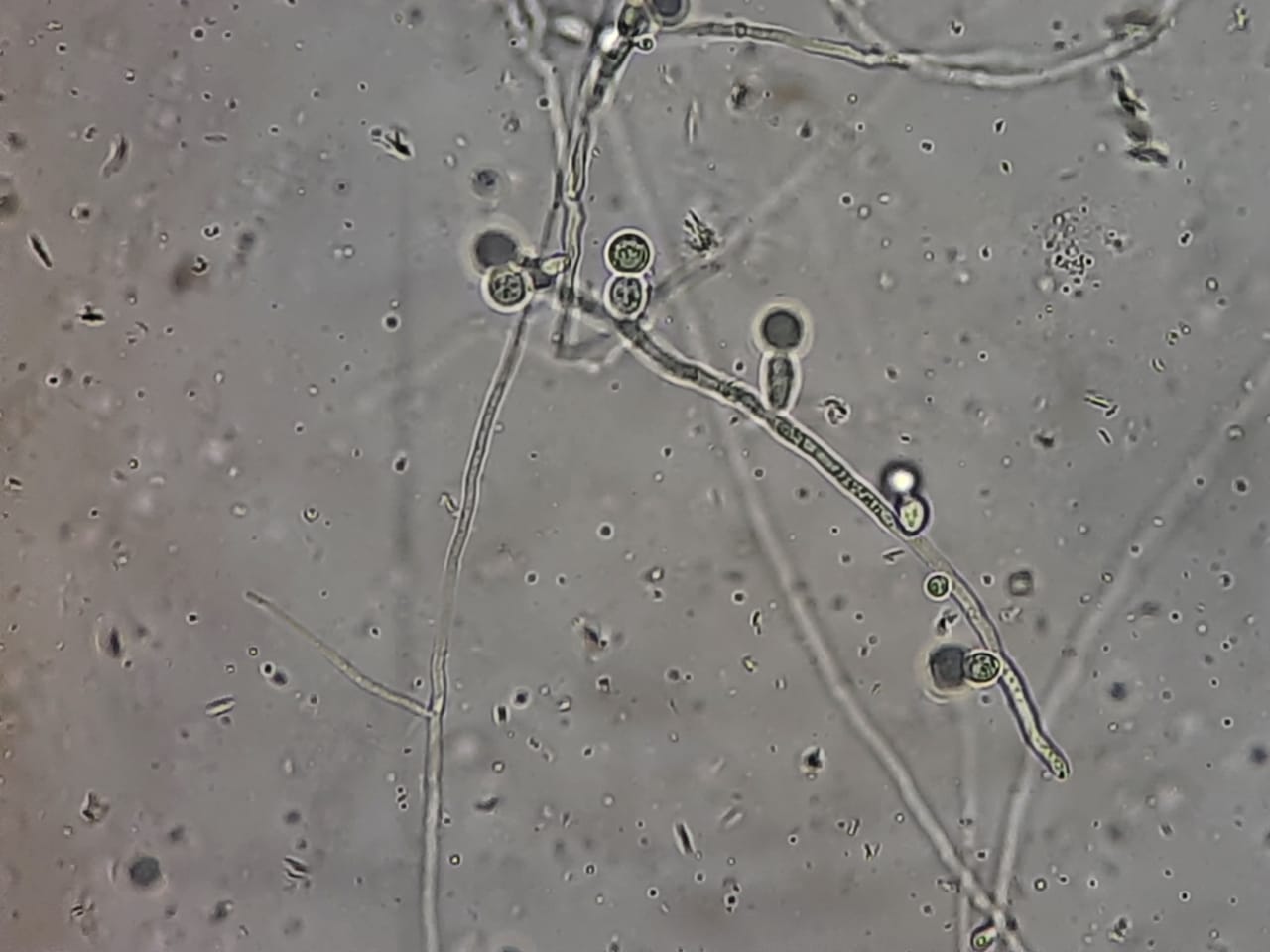
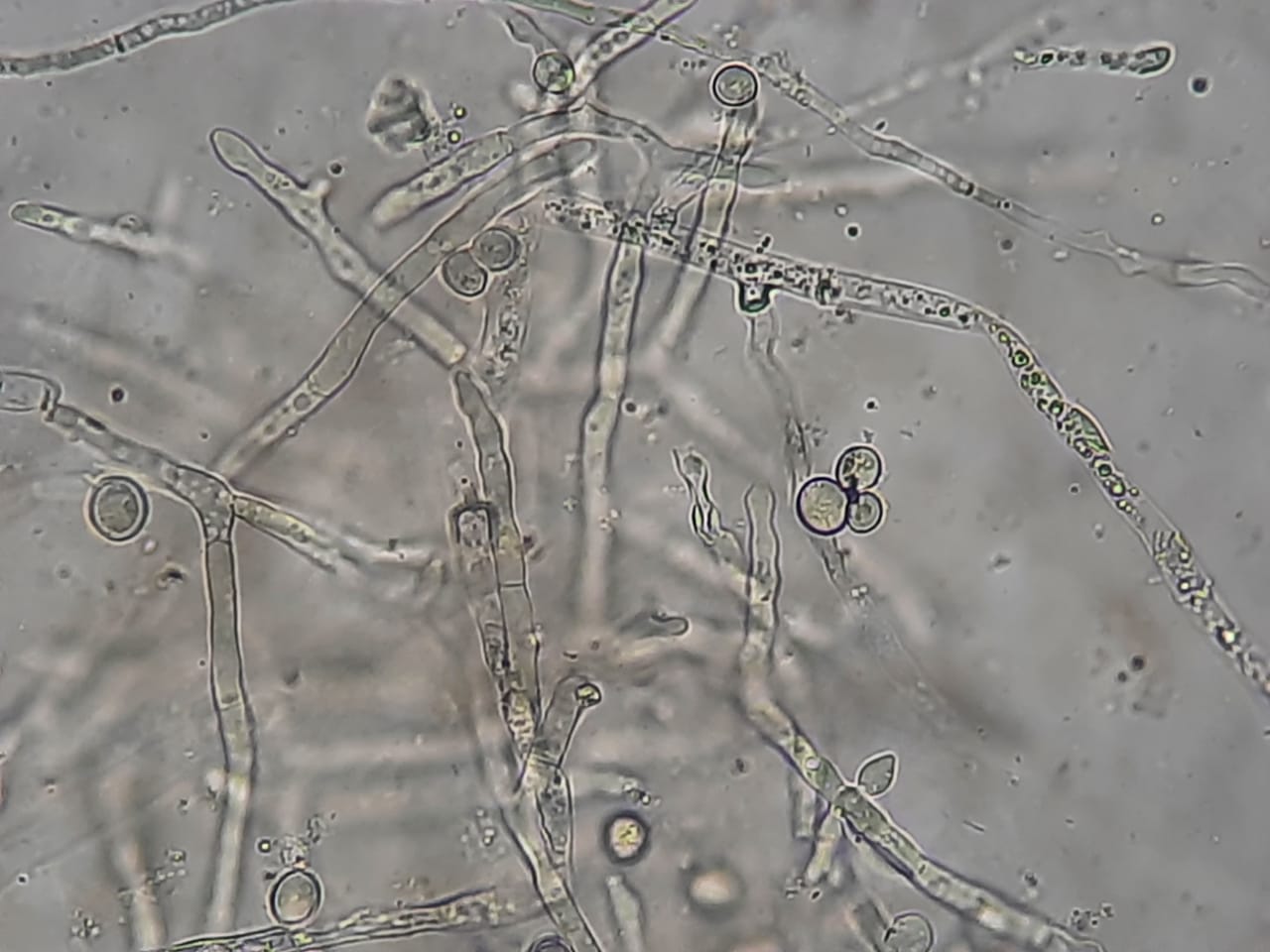
Fungal Elements in KOH Mount of Pleural Fluid Microscopy-Introduction, Possible Fungi Observed in Pleural Fluid KOH Mount, Applications, and Keynotes
Introduction KOH Mount of Pleural Fluid is a rapid, direct microscopic test used to detect fungal elements in suspected pleural infections. A 10–20% Potassium Hydroxide (KOH) solution clears cellular debris, fibrin, and protein content in pleural fluid while preserving chitin-rich fungal structures such as hyphae, …