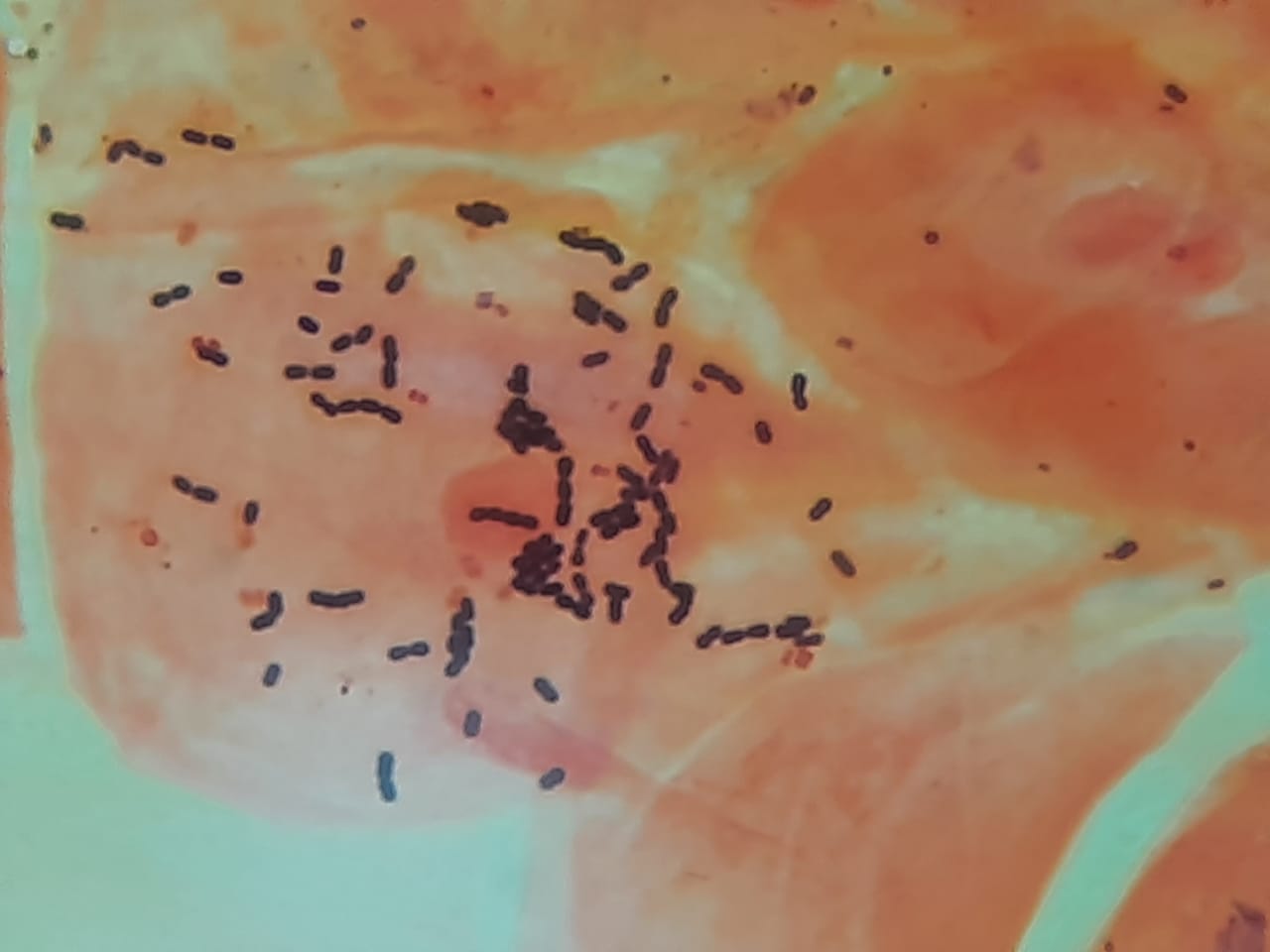
Throat Swab Gram stain: Introduction, Report-Interpretation, Clinical Significance, and Keynotes
Introduction A throat swab Gram stain is a rapid, initial diagnostic test performed on specimens collected from the oropharynx or tonsillar region. It helps to identify bacterial flora, pathogens, and inflammatory response. While culture and molecular methods provide definitive diagnosis, Gram staining offers early guidance …