Fungal Elements in KOH Mount of Bile Microscopy-Introduction, Fungal Elements Observed in Bile KOH Mount, Applications, and Keynotes
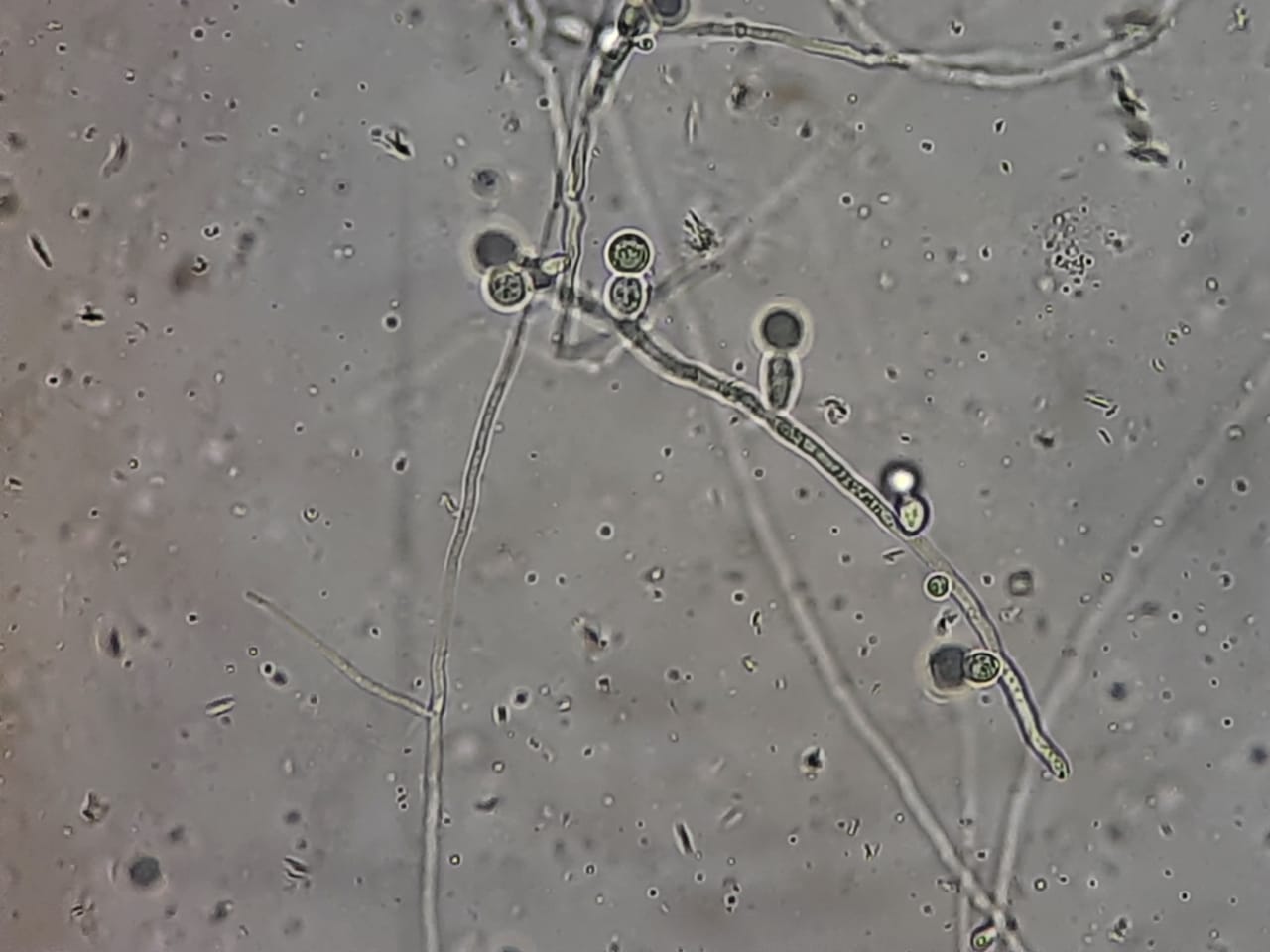
Introduction KOH Mount of Bile is a direct microscopic examination technique used to detect fungal elements in bile fluid collected during ERCP, biliary drainage, cholecystectomy, or liver procedures.Because bile contains mucus, epithelial debris, fats, and pigments, a 10–20% Potassium Hydroxide (KOH) solution is used to …